Who Is The First AI?
The first Artificial Intelligence (AI) was created in the 1950s by computer scientist and mathematician Alan Turing. He developed the Turing Test, which is a way of determining whether or not a computer can think like a human. Turing’s test is still widely used today to determine the level of intelligence of an AI system. Turing also proposed the concept of a “universal machine”, which was the basis for modern computers. His research laid the foundations for the development of computers and programming languages. In the 1960s, AI researchers began to explore ways to make computers better at problem-solving. This led to the development of intelligent agents, which can be used to help automate tasks and make decisions. AI has come a long way since its beginnings, and is now being used in many different ways, from medical diagnosis to online shopping recommendations.
Definition of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a rapidly evolving field of computer science that focuses on the development of intelligent machines that are able to think and act like humans. AI is used to create programs that can solve complex problems, plan, and make decisions independently, and learn from previous experiences. AI has the potential to revolutionize the way we live and work by automating mundane tasks, optimizing systems, and improving customer experience. AI can be found in a variety of applications, from healthcare and finance to robotics and autonomous vehicles. AI is an area of research that is constantly changing and evolving as new technologies and techniques are discovered. Who was the first AI?
The first AI can be traced back to the 1950s, when Alan Turing proposed the Turing Test, which is a model of AI. This test is used to determine if a computer can “think” like a human. AI research has continued to progress since then, with developments in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. Today, AI is being used in a variety of industries, from healthcare to finance. While there is no single individual who can be credited as the “first” AI, Alan Turing is widely acknowledged as a pioneer in this field. His legacy continues to inspire researchers and innovators to push the boundaries of what is possible with AI.
Benefits of AI
The world is rapidly advancing in the field of artificial intelligence (AI). AI has already revolutionized many aspects of our lives, from the way we work to the way we live. AI also has the potential to improve the quality of life of people around the globe. But, who was the first AI?
The answer is, there is no single answer to this question. AI technology has been around since the 1950s, but the first AI system was developed in the early 1980s by John McCarthy, a computer scientist at Stanford University. He developed the first AI system, which was able to respond to human input and learn from its environment. The system was called ELIZA and was the first successful attempt at creating a conversational AI.
Since then, AI has evolved rapidly. Today, AI is used in applications such as natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics. AI systems are able to process large amounts of data quickly and accurately, making it an invaluable tool for businesses and researchers. AI can also be used to automate mundane tasks, allowing humans to focus on more complex problems.
The benefits of AI are numerous. AI systems can improve accuracy and reduce errors in decision-making processes, reducing the cost of mistakes. AI can also help to identify patterns in data that may not be obvious to a human, allowing for more efficient and accurate decision-making. AI can also be used to automate mundane tasks, allowing humans to focus on more complex problems.
In summary, AI has revolutionized the way we work and live. AI systems can be used to automate mundane tasks, identify patterns in data, and make more accurate decisions. AI’s potential to improve the quality of life of people around the globe is immense. The first successful attempt at creating a conversational AI was ELIZA, developed by John McCarthy in the early 1980s. Today, AI is used in a variety of applications, and its potential is still being explored.
Historical Developments in AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been around for centuries, with its roots in the age-old pursuit of creating machines that can think and reason like humans. While the concept of AI has been around for millennia, it was not until the mid-20th century that AI research began to take shape and gain traction from the scientific community. Early AI pioneers such as Alan Turing and Claude Shannon laid the groundwork for AI by creating mathematical models of learning and reasoning. Turing’s famous Turing Test served as the benchmark for AI development, and Shannon’s Information Theory provided the foundation for AI programming.
In the 1950s, AI research began to move from the theoretical phase into the practical realm thanks to the work of John McCarthy, who developed the first programming language for AI, and Marvin Minsky, who founded the first AI laboratory. The development of computers in the second half of the 20th century enabled AI research to move forward at an unprecedented pace. The advent of neural networks and deep learning in the 1980s marked a major milestone in AI development, with machines now able to learn and reason in ways that closely resembled human cognition.
Today, AI is used in a variety of areas and applications, from medical diagnosis and computer vision to robotics and natural language processing. AI technology is continuing to evolve and improve, with researchers and corporations continually pushing the boundaries of what is possible. From self-driving cars to virtual assistants, AI has become an integral part of modern life and is likely to remain so for the foreseeable future.

Examples of AI in Use Today
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a rapidly evolving technology that is transforming the way we live and work. AI’s potential to revolutionize industries, automate processes, and improve decision making is drawing more attention than ever before. Despite its advancements, many people are still unaware of what AI is or how it is used in the real world. To understand the impact of AI, it is important to recognize the historical roots of the technology, and the examples of AI in use today.
The first AI was developed in the 1950s by Alan Turing, a British mathematician and computer scientist. Turing and his team developed a chess-playing AI that was able to beat a human opponent in a game. From this point forward, AI began to develop in leaps and bounds, with the technology being used in a variety of applications.
Today, AI is used in a variety of industries, from healthcare to automotive and finance. In healthcare, AI is used to diagnose and treat medical conditions, to identify patterns in patient data, and to improve patient outcomes. In the automotive industry, AI is used to develop driverless cars that are capable of navigating complex environments. In finance, AI is used to automate processes, such as risk management, portfolio optimization, and fraud detection.
AI is also being applied to a variety of consumer products, such as voice assistants, chatbots, and virtual personal assistants. These products use AI to respond to user queries, provide personalized recommendations, and automate tasks. Additionally, AI is being used to develop new products, such as facial recognition software or smart home automation systems.
Overall, AI has become a powerful force in the modern world. From its historical roots to its current applications, AI is revolutionizing industries and automating processes. As the technology continues to evolve, we will see even more examples of AI in use.
Potential Future of AI
The potential future of AI is an exciting yet daunting prospect. As technology advances, AI is being applied to more and more aspects of our lives. AI is being used to automate mundane tasks, improve decision-making, streamline processes, facilitate communication, and much more. It is no longer a matter of if, but rather when AI will become an integral part of our lives.
AI has the potential to revolutionize the way we work and live. AI can automate processes, allowing for more efficient delivery of goods and services. It can also be used to analyze data and make decisions quickly and accurately, allowing businesses to respond quickly to trends and customer needs. AI can even be used to give personalized recommendations and insights, improving customer experience and satisfaction.
AI also has the potential to revolutionize healthcare, with advances in medical imaging, natural language processing, and robotics. AI can be used to diagnose diseases, predict outcomes, and provide personalized treatment plans, improving the quality and speed of healthcare.
As AI continues to evolve, its potential applications will become more and more diverse. As such, it is important to understand the implications of AI and to ensure that we are capable of managing and regulating it responsibly. From advances in artificial intelligence to the potential implications of AI in healthcare, it is clear that AI has the potential to revolutionize our lives.
AI Ethics and Risks
AI ethics and risks have become increasingly important to consider in the development of Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI has a great potential to revolutionize the way we live, but it’s important to consider the ethical implications and risks that come with it. AI can be programmed to make decisions that may not always be ethical or right, so it’s important to have a set of ethical standards in place when developing and deploying AI. Additionally, there are risks associated with AI, such as data security, privacy issues, and the potential for AI to be used for malicious purposes. It’s important to be aware of these risks and ensure that any AI technology is used responsibly and ethically. AI ethics and risks must be carefully considered when developing and deploying AI technology. By considering the ethical implications of AI and taking the necessary safety precautions, we can ensure that AI technology is used to its full potential without any of the associated risks.
FAQs About the Who Is The First AI?
Q1: Who is the first AI?
A1: The first AI was developed in the early 1950s by British mathematician Alan Turing. Turing developed a test for determining a computer’s ability to think and reason like a human, which became known as the Turing Test.
Q2: What is the Turing Test?
A2: The Turing Test is a test developed by British mathematician Alan Turing to determine a computer’s ability to think and reason like a human. It consists of a human judge conversing with two entities, one human and one machine, that are both hidden from view. If the judge cannot distinguish between the two entities, the machine is said to have passed the Turing Test.
Q3: How does AI work?
A3: AI works by analyzing large amounts of data and using algorithms to learn from that data and make predictions. AI systems can be trained to recognize patterns, identify objects, understand natural language, and take actions based on the data they are given.
Conclusion
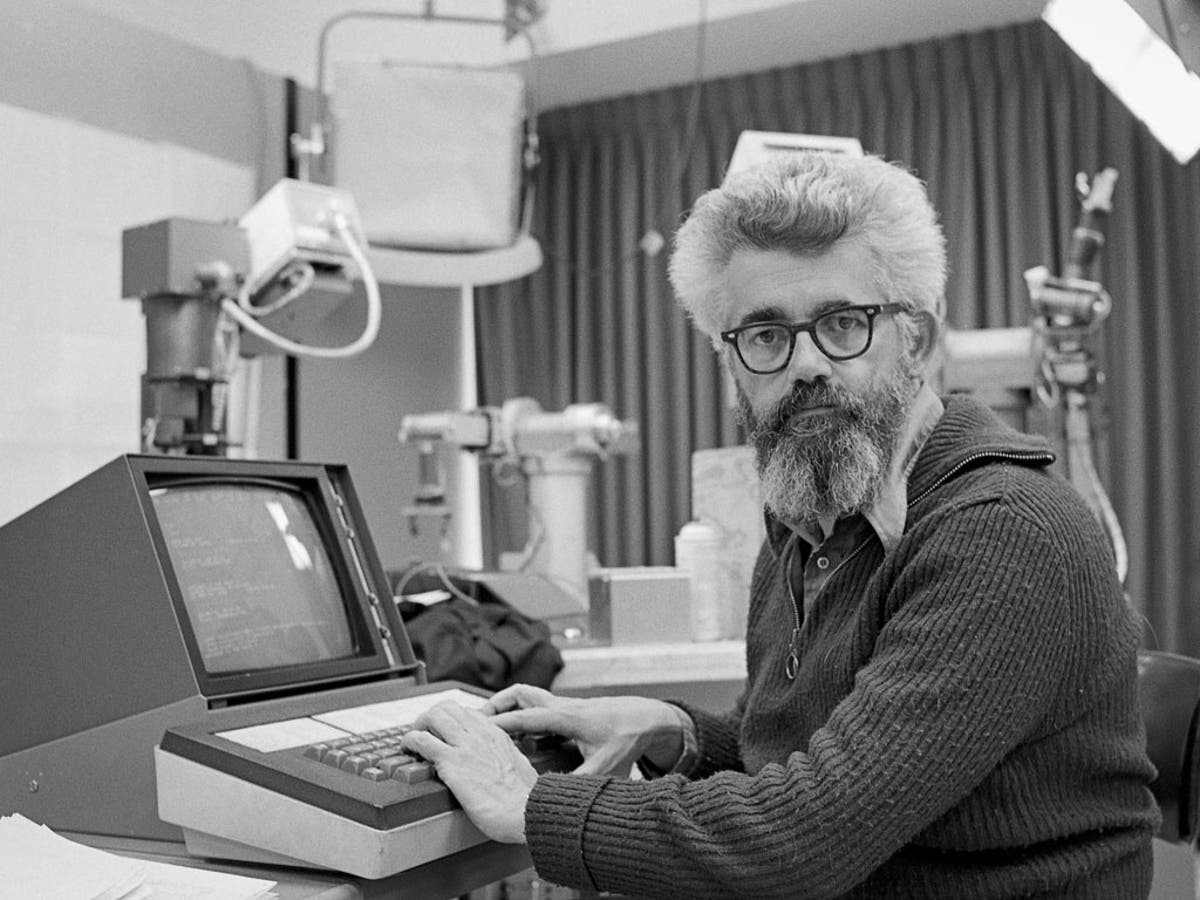
The first AI is widely believed to be a computer program called ELIZA, developed in the 1960s by MIT professor Joseph Weizenbaum. ELIZA was designed to simulate a conversation with a human through natural language processing. ELIZA was the first program to demonstrate the potential of artificial intelligence and has since inspired many other AI projects. Today, AI is used in many areas, from teaching and healthcare to finance and gaming. The possibilities are endless, and the development of AI technology is constantly evolving.