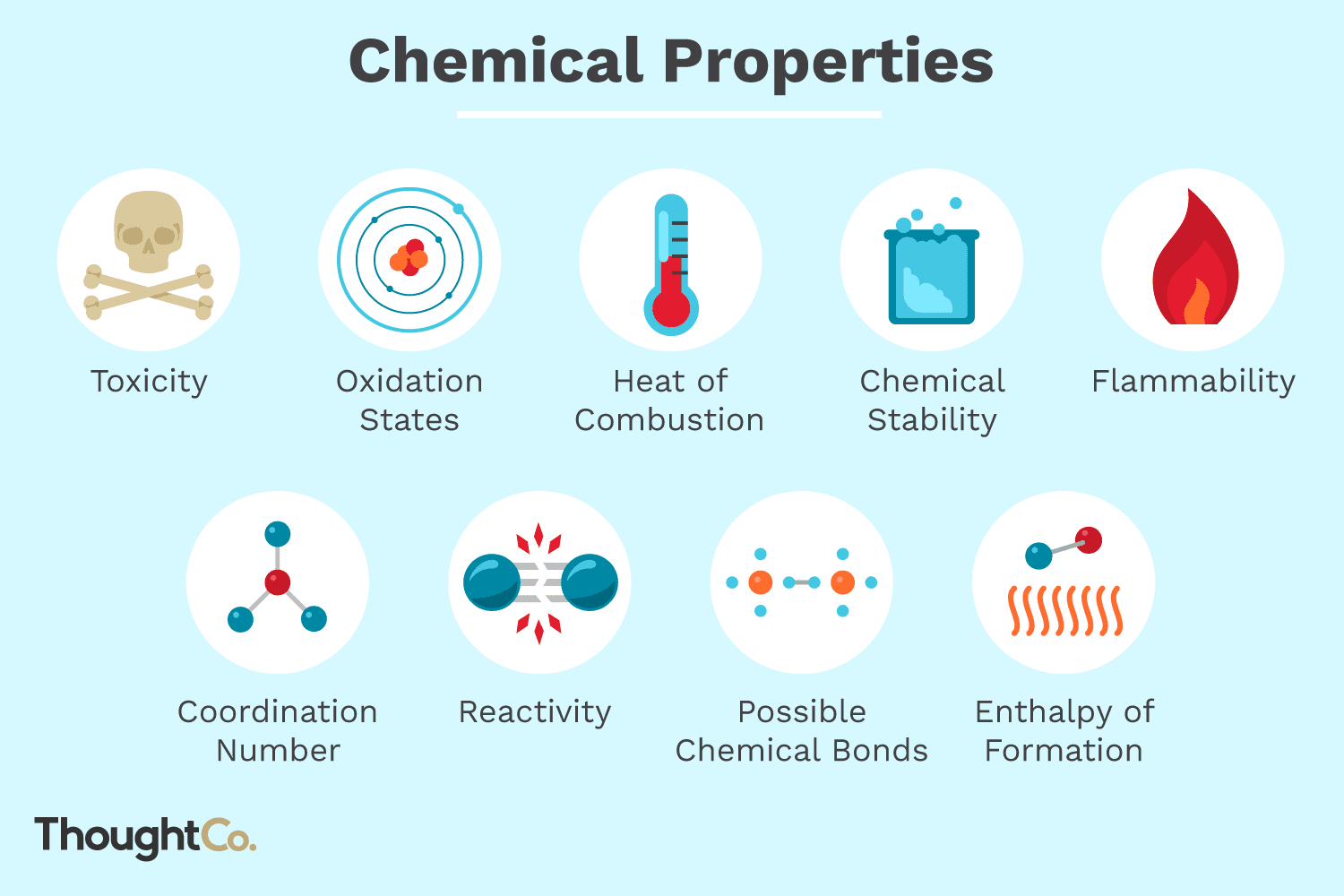
Which Is A Chemical Property?
A chemical property is a property of a substance that can only be observed or measured when it undergoes a chemical change or reaction. Examples of chemical properties include flammability, toxicity, reactivity, and acidity. These properties can be used to identify a substance and to understand how it interacts with other substances.
Definition of Chemical Property
Chemical properties are the characteristics of a substance that can be observed and studied without changing the identity of the substance. They are the result of the chemical composition and structure of the substance and how the substance interacts with other substances. Chemical properties can be physical (such as melting point and boiling point), chemical (such as reactivity or flammability), or thermodynamic (such as enthalpy of formation). Chemical properties can be studied in the laboratory through a variety of experiments and observations. For example, the reactivity of a substance can be tested by combining it with another substance and observing the type and rate of reaction. Flammability can be tested by exposing the substance to an open flame and observing the time it takes for the flame to spread and the intensity of the flame. Chemical properties are essential in understanding the behavior of a substance and its interactions with other substances.
Examples of Chemical Properties
Chemical properties are those characteristics of a substance that can be observed or measured only when the substance is subject to a chemical reaction or change. These properties are often associated with the reactivity of a material and can be used to identify and classify it. Examples of chemical properties include flammability, reactivity, combustibility, acidity, and toxicity.
Flammability is the ability of a substance to catch fire and burn. Substances that are highly flammable can catch fire and burn easily. These substances often have a low flashpoint, meaning they can easily ignite in the presence of a spark or flame. Examples of highly flammable substances include gasoline, alcohol, and acetone.
Reactivity is the ability of a substance to interact with another substance. Substances that are reactive can form bonds with other substances and undergo chemical reactions. For example, sodium is highly reactive because it can easily bond with chlorine to form sodium chloride.
Combustibility is the ability of a substance to burn. Combustible materials are materials that can catch fire and burn quickly. Examples of combustible materials include wood, paper, and coal.
Acidity is the ability of a substance to produce hydrogen ions in a solution. Acids are substances that produce hydrogen ions in a solution and have a pH less than 7. Examples of acids include hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and acetic acid.
Toxicity is the ability of a substance to cause harm to living organisms. Toxic substances are materials that can cause injury, illness, or death when ingested or inhaled. Examples of toxic substances include lead, arsenic, and mercury.
Characteristics of Chemical Properties
Chemical properties are the traits of a substance that are revealed when it is subjected to a chemical reaction. These properties can be used to differentiate one substance from another and to identify the elements and compounds that make up a particular substance. Chemical properties include the ability of a substance to react with other substances, the way it changes when it is exposed to different conditions, and the type of energy it releases when it is broken down. In addition, the physical characteristics, such as color, odor, and density of a substance, can also be used to describe its chemical properties.
Understanding the chemical properties of a substance can be useful in a variety of applications, such as medicine, environmental science, and industrial production. By identifying the properties of a substance, scientists can determine how it will interact with its environment, how it will react with other substances, and what kind of energy it will release when it is broken down. This information can be used to develop new products, analyze the effects of certain chemicals on the environment, and develop treatments for diseases.
Chemical properties can also be used to identify the elements that make up a particular substance. By understanding the chemical properties of a substance, scientists can determine the type of elements present in a substance and how those elements interact with one another. This information can be used to develop new materials, create new compounds, and improve existing products.
Overall, chemical properties are a key element in understanding the makeup of a substance and how it interacts with its environment. By understanding the chemical properties of a substance, scientists can develop new products, analyze the effects of certain chemicals on the environment, and develop treatments for diseases.

The Relationship between Chemical and Physical Properties
Chemistry is a branch of science that studies the composition and properties of matter. Chemical properties are characteristics of a substance that can be observed and measured when the substance undergoes a chemical reaction, and physical properties are characteristics of a substance that can be measured without changing the composition of the substance. Together, chemical and physical properties are used to identify a substance and understand its properties.
Chemical properties provide insight into the behavior of a substance and how it interacts with other substances. For example, the flammability of a substance is a chemical property because it can only be measured by observing the substance burning. On the other hand, physical properties are more tangible and can be observed without any chemical reactions. Examples of physical properties are color, density, hardness, boiling point, and melting point.
Chemical and physical properties are essential for classifying and understanding the properties of a substance. They are used to identify substances, determine their behavior, and predict how they will react with other substances. By understanding the relationship between chemical and physical properties, chemists and other professionals can further their understanding of the world around them.
Identifying Chemical Properties in the Laboratory
Chemical properties are an important part of understanding the behavior of matter in the laboratory. These properties are different from physical properties, which are able to be measured without changing the composition of the substance. Chemical properties include combustibility, reactivity, and toxicity, and they are typically determined through experiments. In the laboratory, scientists can use a variety of techniques to identify chemical properties, such as observing reactions when different substances are mixed or exposed to heat, cold, or light. From these observations, scientists can determine the combustibility, reactivity, and toxicity of the substances. In addition, they may also be able to make predictions about a substance’s behavior when exposed to different temperatures, pressures, and concentrations of other chemicals. By understanding chemical properties, scientists can make informed decisions about chemical safety and use, as well as develop new materials.
Conclusion
Chemical properties are physical and chemical characteristics of a substance that can only be observed or measured by performing a chemical change or reaction. They are used to describe the reactivity of materials in a variety of chemical reactions. Chemical properties are the most important criterion for determining the physical and chemical behavior of a material. It is important to understand the differences between various chemical properties in order to make accurate predictions about how a material will behave in a given environment. The knowledge of chemical properties is essential for scientists and engineers to develop new materials and technologies.
FAQs About the Which Is A Chemical Property?
1. What is a chemical property?
A chemical property is a characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured only by a chemical reaction. Examples of common chemical properties include flammability, reactivity, and toxicity.
2. How is a chemical property different from a physical property?
A physical property is a characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance, while a chemical property is a characteristic of a substance that is only observed or measured by a chemical reaction.
3. What are some examples of chemical properties?
Some examples of common chemical properties include flammability, reactivity, acidity, pH, and toxicity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a chemical property is a characteristic of a substance that is only observable when the substance is undergoing a chemical reaction. It is determined by the chemical composition of the substance and is not affected by physical changes, such as changes in temperature or pressure. Chemical properties are often used to identify and differentiate between different substances.