Which Channel Width Is Best For Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi is an essential part of the modern lifestyle, allowing us to stay connected to the Internet wherever we go. With so many different types of Wi-Fi networks available, it can be confusing to figure out which channel width is best for your needs. The answer can depend on a variety of factors, such as the type of network you’re using, the type of devices you have, and the number of devices connected to the network. This guide will outline the different types of channel widths, the pros and cons of each, and the best channel width for your Wi-Fi network.
Overview of Wi-Fi Channel Width
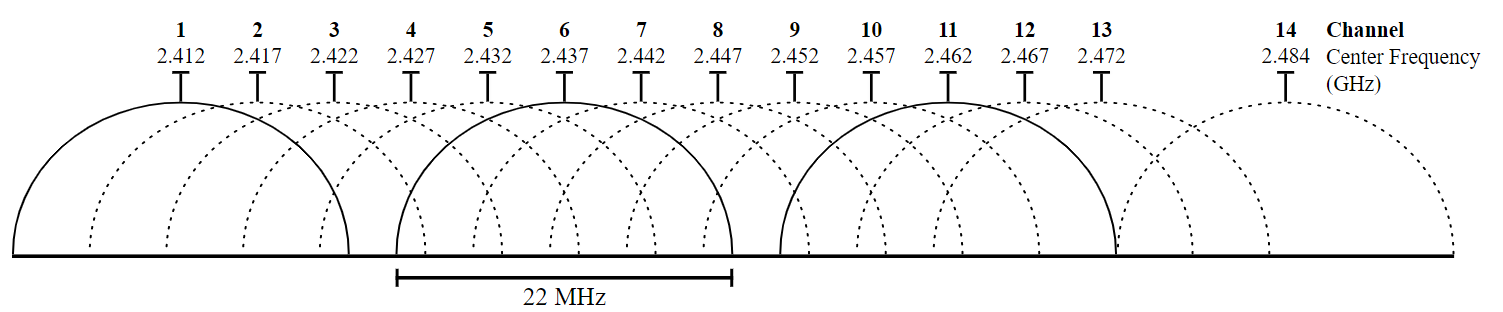
When it comes to setting up your Wi-Fi network, choosing the right channel width is essential. It is important to understand the different channel widths available and their respective advantages and disadvantages. Wi-Fi channel width broadly refers to the amount of bandwidth allocated to the signal, affecting the speed and range of the connection. Wi-Fi transmission speeds are determined by the channel width, and the router’s capabilities. The most common channel widths are 20MHz, 40MHz, and 80MHz, but it can range anywhere from 20MHz to 160MHz.
20MHz is the narrowest channel width and is the default setting for most routers. It is suitable for small networks, but it is not the most efficient channel width for streaming HD video or transferring large files. 40MHz is the most popular channel width, but it is best for short-range connections and low-density networks. 80MHz is the widest channel width and is best used in high-density networks and for streaming HD video.
To maximize Wi-Fi performance, it is important to understand the needs of the network and the capabilities of the router. Choosing the right channel width will ensure that the network is optimized to transfer data quickly and reliably. By understanding the different channel widths and their respective advantages and disadvantages, it is possible to set up a Wi-Fi network that meets the needs of the network and maximizes its performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Channel Widths
Wi-Fi is essential for staying connected, but it can be tricky to optimize your network for the best performance. A key factor in the performance of your Wi-Fi is the channel width, which affects the speed of your connection and how many users your network can handle. Different channel widths come with their own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to understand the different types and determine the best one for your network.
The most common channel widths are 20, 40, and 80 MHz. A 20 MHz channel width is the most common and provides the greatest compatibility with older devices. However, it does not support the highest speeds and can only support a small number of users. A 40 MHz channel width is a good compromise between performance and compatibility. It supports higher speeds and more users than 20 MHz, but not as many as 80 MHz. An 80 MHz channel width offers the highest speeds and is best for networks with many users. However, it is not compatible with all devices.
The best channel width for your Wi-Fi network depends on your needs. If you’re looking for the highest speeds and greatest number of users, an 80 MHz channel width is the best choice. But if you have older devices or fewer users, a 20 MHz or 40 MHz channel width may be a better option. Ultimately, it’s important to understand the advantages and disadvantages of each channel width so you can choose the best one for your network.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Channel Width
Choosing the right Wi-Fi channel width is essential for optimal wireless performance. But there are a variety of factors to consider when selecting the best channel width for your needs. The most common channel widths used for Wi-Fi networks are 20MHz, 40MHz, and 80MHz.
When deciding on the best channel width for your network, you’ll need to take into account the type and number of devices connected to your Wi-Fi router. If you have several devices connected to your Wi-Fi network, a wider channel width may provide more bandwidth for these devices to share. On the other hand, if you have fewer devices, a narrower channel width may be more efficient.
The environment in which your Wi-Fi network operates can also play a role in deciding the best channel width. If you are in an area with a lot of interference from other Wi-Fi networks, a narrower channel width may be more beneficial. This is because the smaller channel width will help to reduce interference from nearby networks.
Finally, the type of Wi-Fi network you are using will also affect which channel width is best. If you are using 802.11ac, a wider channel width is recommended. However, if you are using 802.11n or older, a narrower channel width may be more suitable.
By considering the type and number of devices connected to your network, the environment in which your network operates, and the type of Wi-Fi network you are using, you can make an informed decision on which channel width is best for your Wi-Fi network.

Common Channel Widths and Their Usage
When it comes to Wi-Fi, the channel width is an important factor. It affects the performance of your network, the speed of your connection, and the range of your signal. But which channel width is best for Wi-Fi?
Understanding the different types of channel widths is key when it comes to selecting the best option for your network. The most common channel widths are 20MHz, 40MHz, and 80MHz. Each has its own purpose and benefits.
A 20 MHz channel is the narrowest channel width available on Wi-Fi networks. This channel width is best for congested networks, as it uses less bandwidth and is less likely to suffer from interference. It is also the most common channel width used for the 2.4 GHz frequency.
A 40MHz channel is wider than a 20MHz channel and is best used in the 5GHz frequency range. This channel width is ideal for streaming high-definition content, as it offers the fastest speed and fewest latency issues.
An 80MHz channel is the widest channel width available on Wi-Fi networks. It is best used for large-scale networks with many devices. An 80MHz channel gives you the highest bandwidth and the most range, which is ideal for businesses and other large organizations.
By understanding the different channel widths and their usage, you can make an informed decision when it comes to selecting the best channel width for your Wi-Fi network. With the right channel width, you can maximize your network performance and enjoy the best possible wireless connection.
Impact of Bandwidth Limitations on Wi-Fi Performance
Choosing the appropriate channel width for Wi-Fi is essential to ensure optimal performance. It is important to note that while a wider channel width can provide more data throughput, it can also lead to an increase in interference and slower speeds. To make matters worse, the wider channel widths are not supported by older devices. This can lead to a decrease in performance due to the channel width limitations on those devices.
When selecting a channel width for your Wi-Fi network, it is important to remember that the wider the channel width, the more interference you will encounter. This will reduce the range of your Wi-Fi signal and the speed of your connection. On the other hand, a narrower channel width will provide better coverage and faster speeds but with a lower data throughput. It is important to choose a channel width that is appropriate for your needs and compatible with all of your devices.
In addition, it is important to consider the maximum transmission rate of the router when selecting a channel width. The higher the maximum transmission rate, the more data the router can handle and the more data throughput can be achieved. If your router has a maximum transmission rate of less than 300 Mbps, then a 20 MHz channel width should be sufficient. However, if the maximum transmission rate is higher than 300 Mbps, then a 40 MHz channel width is recommended.
Overall, the choice of channel width is based on the needs of the user, the devices in use, and the maximum transmission rate of the router. Using the right channel width can help ensure optimal Wi-Fi performance and the best user experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the right Wi-Fi channel width is essential for obtaining optimal network performance. While 20 MHz is the most common width for 2.4GHz networks, 40MHz is the most commonly used width for 5GHz networks. Higher channel widths offer faster speeds but come with the risk of increased interference. Ultimately, the best channel width for your Wi-Fi network depends on your individual network requirements and environment. To ensure you’re getting the best performance, it’s important to experiment with different channel widths and monitor your network performance. Additionally, if your router supports it, using a combination of 20 MHz and 40MHz can be a great way to balance speed and reliability.
FAQs About the Which Channel Width Is Best For Wi-Fi?
1. What is the difference between 20MHz and 40MHz channel widths?
Answer: The principal difference between 20MHz and 40MHz channel widths is the amount of data that can be transmitted over each channel. A 20MHz channel width can transmit up to 54 Mbps, while a 40MHz channel width can transmit up to 150 Mbps.
2. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a 40MHz channel width?
Answer: The main advantage of using a 40MHz channel width is that it can transmit more data than a 20MHz channel width. However, it can also cause interference with neighboring networks, as it takes up more bandwidth.
3. Should I use a 20MHz or 40MHz channel width for my Wi-Fi network?
Answer: The best channel width for your Wi-Fi network will depend on your particular network setup and usage. If you are using a single device or have a small number of devices, then a 20MHz channel width should be sufficient. However, if you have multiple devices and require higher data throughput, then a 40MHz channel width may be a better option.
Conclusion
It is difficult to definitively say which Wi-Fi channel width is best, as it depends on a variety of factors such as network type, environment, and device capabilities. Generally, wider channel widths provide faster speeds, but they also increase interference and can reduce range. The best channel width for any given Wi-Fi network will depend on the user’s specific needs.