What Slows WiFi The Most?
WiFi is a critical part of modern life, but sometimes it can be slow and unreliable. There are several factors that can cause a WiFi connection to slow down, such as physical obstructions, interference from other devices, and outdated hardware. Understanding what slows WiFi the most is key to improving your connection and enjoying the full benefits of your network. In this article, we’ll discuss the most common causes of slow WiFi and how you can improve your connection.
What is WiFi?
WiFi is a technology that uses radio waves to provide network connectivity between computers, phones, and other wireless-enabled devices. It allows users to connect to the internet without the need for cables or wires. WiFi has become an indispensable part of our lives, making everything from streaming movies to checking emails much more convenient. But, what slows WiFi the most?
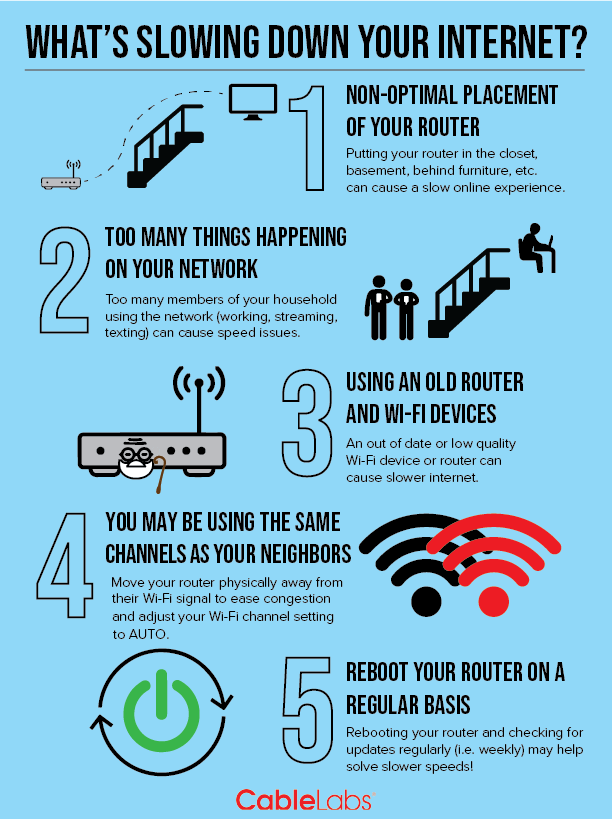
WiFi speed is affected by a number of factors, such as the router’s distance from the device, the number of users connected to the same network, and interference from other wireless signals. Additionally, physical objects such as walls, furniture, and other obstructions can interfere with the signal, causing it to slow down. Poor network performance can also be caused by outdated hardware or software, incorrect settings, and even viruses.
Understanding what slows down your WiFi is the first step to improving it. By taking a few simple steps such as upgrading your router, relocating it for better signal, and using repeaters or extenders, you can significantly increase your connection speed. Additionally, you should make sure your devices have the latest software updates installed, and run regular virus scans to protect your network from malicious programs.
In conclusion, WiFi speed can be affected by a number of factors, from physical obstructions to outdated hardware. By taking a few simple steps, you can significantly improve the performance of your network.
Factors Affecting WiFi Speed
WiFi is the backbone of modern day connectivity, giving us the freedom to access information, entertainment, and communication from virtually anywhere. However, there are a number of factors that can significantly slow down your home or office WiFi connection. Understanding these factors and taking the appropriate steps to mitigate them can help ensure you get the most out of your WiFi service.
The most common factor that affects WiFi speed is interference from other devices. This can be anything from microwaves, cordless phones, and baby monitors to other WiFi networks in the area. As these devices emit their own radio waves, they can interfere with the signal from your router, resulting in a slower connection. To reduce interference, try to keep your router away from other WiFi networks and electronic devices. Additionally, make sure your router is up to date with the latest firmware.
Distance is another factor that can slow down your WiFi. The further away your device is from the router, the weaker the signal will be, resulting in slower speeds. Try to position your router in an open area with minimal walls and other obstacles that can block or weaken the signal.
Another factor that can affect speed is bandwidth. If there are too many devices connected to the same network, it can cause a bottleneck, resulting in slower speeds. To combat this, try limiting the number of devices connected to your network or investing in a more powerful router.
Finally, the type of router you are using can significantly affect WiFi speeds. If you have an older router, it may be time to upgrade to a more powerful model that can support the latest standards. Additionally, if you want to maximize your speeds, consider investing in a mesh network system which spreads the signal throughout your home.
By understanding these factors and taking the appropriate steps to mitigate them, you can ensure you get the most out of your WiFi service.
Interference from Other Networks
When it comes to understanding what slows down WiFi, interference from other networks is an important factor to consider. As more and more devices are connected to the same network, the airwaves become crowded, making it difficult for the router to communicate with each one. This overcrowding can cause interference from neighboring networks, which can result in slower speeds. The interference may come from other wireless networks, cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, microwaves, or even radio towers. To reduce the interference, users should switch to a different channel or use a signal booster to increase the signal strength. Additionally, using the 5Ghz frequency can help to reduce interference and improve wireless connection speeds.

Distance from the Router
WiFi revolves around the router – it’s the heart of the network and the source of the signal. The farther away you are from your router, the weaker the signal will be. This means that the speed and reliability of your connection decrease as you move further away from the router. This is especially true with older routers, as they can’t send out a strong enough signal to cover a large distance. If you find yourself in a spot where your WiFi isn’t working as it should, consider moving closer to the router. While it might not be the most convenient solution, it will help to ensure that you’re getting the best possible connection.
Obstructions to Signal Strength
WiFi signals can be weakened or blocked by obstacles such as walls, furniture, and other objects, as well as interference from other wireless devices. These obstacles interfere with the signal strength, causing the network to slow down or even drop off completely. To ensure you have optimal signal strength, it’s important to understand what might be blocking or weakening your WiFi signal and take steps to reduce any blockages.
The type of material the obstruction is made of is a major factor in how much it will affect your WiFi signal. For example, a concrete wall will block more signal than a wooden wall. Even materials like metal, glass, and plaster can reduce signal strength. Additionally, the frequency of the signal can also affect how much it will be blocked, as higher frequencies are more likely to be absorbed or reflected.
The distance between your device and the router can also have an effect on the signal strength. The further away your device is, the more likely you are to experience a weak or blocked signal. Even the orientation of the router can affect the signal, as the signal is usually strongest when the antenna is pointed in the direction of your device.
Finally, interference from other wireless devices can also weaken your WiFi signal. Wireless devices such as phones, microwaves, and certain types of home security systems can all interfere with your router’s signal. To reduce this type of interference, you should look for a router with a frequency that is less likely to be disturbed by other devices.
By understanding what slows WiFi the most and taking the necessary steps to reduce any obstructions, you can ensure that your network runs smoothly and reliably.
Upgrading Your Router or Modem
WiFi speeds can be affected by a variety of factors, some of which are within our control. One of the most effective ways to improve your WiFi speeds is to upgrade your router or modem. Many people don’t realize that a new router or modem can make a huge difference in terms of performance. Older routers and modems can be slow and outdated, leading to slow WiFi speeds. Upgrading your router or modem can not only improve your WiFi speeds, but it can also provide a more secure connection and better overall performance. It’s important to do your research and make sure you buy a router or modem that is compatible with your current internet service. Additionally, you should consider purchasing a router or modem that supports dual-band technology, which can help to reduce interference and improve the connection. With the right router or modem, you can quickly and easily upgrade your WiFi speeds.
FAQs About the What Slows WiFi The Most?
Q1: What can I do to reduce my WiFi speed?
A1: To reduce your WiFi speed, try reducing the number of devices connected to your WiFi, as each device uses some of the bandwidth available. You should also check the physical location of your router and make sure it is in an open area with no obstructions that could interfere with the signal. Additionally, make sure that your router is up-to-date with the latest firmware and that all connected devices are using the latest wireless standards.
Q2: How can I improve the signal strength of my WiFi?
A2: To improve the signal strength of your WiFi, try moving the router to a more central location in your home or office. Additionally, you can purchase a WiFi range extender or repeater to broaden the coverage area of your network. You should also check for any interference from neighboring networks and make sure that your devices are using the latest wireless standards.
Q3: Can outdated wireless standards slow down my WiFi?
A3: Yes, outdated wireless standards can reduce the speed of your WiFi. To ensure that your devices are using the latest wireless standards, make sure they are updated with the latest software and firmware. Additionally, you should check that the router is also up-to-date with the latest firmware and that it is using the latest wireless standards.
Conclusion
In conclusion, WiFi speed is mainly determined by the router’s performance, the number of users connected, and the type of internet connection. Other factors such as physical obstructions, interference from other electronic devices, and the age of the router can also affect WiFi speed. While these factors can slow down WiFi performance, it is possible to optimize the router settings and environment to improve the speed and reliability of the connection.