What LTE Means?
LTE stands for Long Term Evolution and is a 4G mobile communication standard used in wireless networks. It is an advanced technology that is used to provide higher data rates and greater capacity than other mobile communication standards, such as 3G. LTE is capable of providing speeds of up to 300 Mbps for downloads and 75 Mbps for uploads. It is also capable of supporting multiple users in a single network. LTE is the most widespread standard in use today, and is used by most major mobile providers around the world.
What is LTE?
LTE stands for Long Term Evolution and is the latest generation of mobile communication technology. It is the most advanced technology available today for mobile data transmission. LTE is used by most major mobile networks globally and is the preferred choice for high-speed, reliable data transmission. LTE enables higher data rates, larger capacity, and improved coverage than older generations of mobile technology. It is faster than 3G, which means that users can experience faster download speeds and improved streaming services. LTE also offers more efficient bandwidth usage and increased network capacity, which is beneficial for customers who need to use more data. LTE also offers better voice quality and improved system stability. In addition, LTE also provides improved security protocols that protect customers’ data and privacy. All in all, LTE is a powerful, reliable, and secure mobile technology that is becoming the standard for wireless data transmission.
How Does it Work?
LTE, or Long-Term Evolution, is the 4G standard for wireless communication used by cellular networks around the world. LTE is the successor to 3G, offering faster data speeds, improved performance, and better quality of service. But how does LTE work?
LTE technology utilizes multiple frequency bands to allow more data to be transmitted at once, and uses advanced antenna technology for improved signal strength and range. It also uses advanced coding techniques to allow data to be transmitted over the same frequency bands multiple times, improving data throughput. On the user side, LTE supports multiple simultaneous connections, meaning users can access multiple services at once without slowing down their connection.
LTE is also optimized for mobile devices, meaning it can adjust its data transmission rate based on the device being used. This way, users can get the best performance even in areas with poor reception. Additionally, LTE networks are constantly being upgraded to support the latest wireless devices and technologies, ensuring users are always getting the best experience.
In summary, LTE technology is becoming the standard for wireless communication due its improved performance and quality of service compared to 3G. It is optimized for mobile devices, can support multiple simultaneous connections, and is constantly being upgraded to support the latest wireless technologies.
Benefits of LTE
LTE (Long Term Evolution) is a critical component of modern network technology. It is a broadband technology used by mobile providers to provide users with faster data speeds and better coverage. LTE has revolutionized the mobile landscape, providing users with a better experience and enhancing their mobile data capabilities. There are numerous benefits associated with LTE, which include improved speeds, better coverage, and improved battery life.
For users, LTE provides faster speeds than 3G technology and is capable of handling a variety of data-heavy tasks, such as streaming video and downloading large files. LTE also offers better coverage than 3G, reaching more areas and providing users with better signal strength and fewer dropped calls. Additionally, LTE can provide improved battery life, as it uses less energy than 3G networks, allowing users to get more out of their device.
For mobile providers, LTE allows them to provide users with a better experience and more reliable coverage. LTE also allows providers to offer an array of services and applications, such as HD video streaming and faster data speeds. This can help providers to differentiate themselves from their competitors and attract more customers.
Overall, LTE is a powerful technology that provides numerous benefits to both users and mobile providers. With faster speeds, better coverage, and improved battery life, LTE is an essential component of modern network technology. By utilizing LTE, mobile providers can offer their customers an enhanced experience and better coverage.
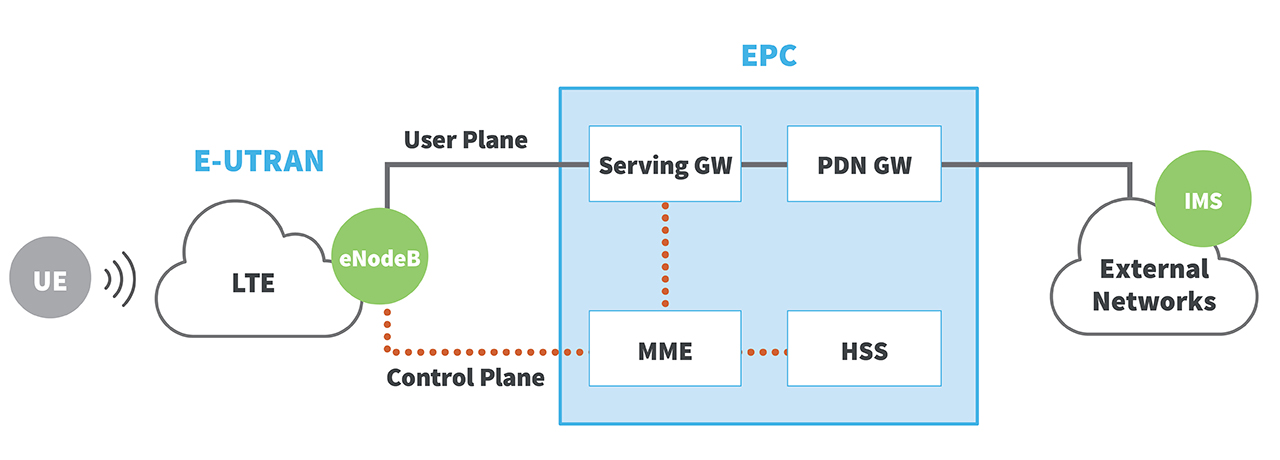
Challenges of LTE
The wireless world has undergone a major transformation in recent years, and LTE (Long Term Evolution) is at the forefront of this revolution. It is a 4G mobile communication standard that has ushered in faster data speeds and increased network capacity. But despite its many benefits, LTE poses some challenges for mobile companies.
One of the biggest challenges of LTE is the cost of deployment. LTE requires significant investments in infrastructure, such as base stations and antennas. Additionally, LTE networks require more spectrum than 3G networks, which can be expensive to acquire. This makes it difficult for some companies to justify the cost of deploying an LTE network.
Another challenge is interoperability. LTE networks are not compatible with 3G networks, which means that devices must be upgraded in order to work with LTE. This can be an expensive and time-consuming process for mobile companies.
Finally, LTE networks are more vulnerable to interference. Because of its higher frequency, LTE is more susceptible to external interference from other devices or objects. This can lead to degraded performance and dropped calls.
Overall, LTE has enabled wireless networks to reach faster speeds and increased capacity, but its implementation comes with some challenges. The cost of deployment, interoperability issues, and susceptibility to interference can all be difficult to manage. Companies must address these challenges in order to maximize the benefits of LTE.
Future of LTE
LTE, or Long Term Evolution, is the fourth generation (4G) of mobile telecommunications technology which provides faster internet speeds and improved coverage compared to previous generations. As the demand for improved data speeds continues to grow, LTE has become a popular choice for mobile operators and consumers alike. The development of 5G networks has accelerated the growth of LTE networks, which are now the largest mobile broadband technology in the world. LTE offers higher data rates, faster download speeds, and lower latency than previous generations of mobile networks. With the development of 5G, LTE networks will become increasingly important as they provide the backbone for 5G networks. 5G networks will provide even faster speeds and improved coverage, but they will require LTE networks to provide the backbone for their data. As such, LTE networks will continue to be a key part of the mobile communications landscape for the foreseeable future. LTE technology provides a reliable and secure connection for users and operators alike, and its evolution has played a key role in driving the growth of mobile technology.
Practical Applications of LTE
Long-Term Evolution (LTE) is a communication protocol that enables high-speed data transmission, and is the fourth-generation (4G) mobile communication technology. This technology is used by mobile operators to provide improved coverage and faster data speeds for their customers. But what does LTE mean and how is it being used in the real world?
The LTE network is designed to enable faster speeds and more reliable connections than those offered by 3G networks, allowing users to access the internet faster. This means that users can experience better streaming quality when watching videos or listening to music, as well as improved performance when playing online games. Additionally, LTE networks allow for larger file sizes to be sent and received, meaning that users can send and receive larger files, such as photos and videos, quicker.
Another practical application of LTE is in the Internet of Things (IoT). With the increased speed and reliability of LTE, many IoT devices can be connected to the internet, such as smart home appliances, sensors, and connected cars. This allows for users to monitor and control their devices from anywhere in the world, providing increased convenience and security.
LTE is also being used for a range of other applications in the real world, including machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, wireless hotspots, public safety networks, and home automation. As the technology continues to develop, it is likely that we will see more and more practical applications of LTE in the coming years.
FAQs About the What LTE Means?
1. What does LTE mean?
Answer: LTE stands for Long Term Evolution and is a type of 4G wireless communication technology. It is the fastest type of mobile network currently available, allowing users to access the internet at speeds up to 10 times faster than 3G networks.
2. What are the benefits of using LTE?
Answer: The main benefit of using LTE is that it provides faster internet speeds, allowing users to download content quickly and stream videos without buffering. Additionally, LTE networks offer better coverage than 3G networks, meaning that users can access the internet more reliably in a variety of locations.
3. What devices are compatible with LTE networks?
Answer: Most modern smartphones and tablets are compatible with LTE networks. Many of the latest iPhones and Android devices come with LTE capabilities as standard, but it is important to check the specifications of your device before signing up for a plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, LTE stands for Long Term Evolution and is a 4G technology for mobile communications. It is designed to provide high speed data access, voice, messaging, and other services. LTE is faster than 3G and provides additional features such as faster speeds, more efficient use of spectrum, and lower latency. It is the foundation for most mobile networks and is becoming the standard in the mobile industry.