What Is Property Of Matter?
Property of matter is the set of characteristics that describe an object or substance and determine how it behaves in different situations. These properties can include physical properties, such as color, density, and boiling point; chemical properties, such as reactivity and solubility; and biological properties, such as toxicity and digestibility. By understanding the properties of matter, scientists can better understand the behavior of substances in different situations and use them in a variety of applications.
Definition of Matter
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. This includes both physical and chemical elements, such as rocks, gases, liquids, and energy. It is the physical form of the universe, what makes up the observable universe and everything in it. All matter is composed of atoms, which are the building blocks of all matter. Matter can exist in three states: solid, liquid, and gas.
When something is formed, it is called matter. All matter is made up of particles, which are held together by forces. These particles have different properties, such as size, shape, and mass. The properties of matter determine how it interacts with other matter and how it behaves in different environments. For example, water is a liquid at room temperature, but it can be solidified into ice at lower temperatures.
The properties of matter can be altered to create new forms of matter. For example, chemical reactions can change the properties of compounds and elements, creating new substances. This process is called chemical synthesis.
Overall, matter is the physical form of the universe and everything in it. It is composed of particles that have different properties, and it can be altered to create new forms of matter. Its properties determine how it interacts with other matter, and how it behaves in different environments.
Different States of Matter
Matter can exist in different states, each with its own distinct physical properties. Solids, liquids, and gases are the three most common states, but matter can also take on other forms, such as plasma, Bose-Einstein condensates, and quark-gluon plasmas. Each state of matter is governed by different laws of physics, such as the laws of thermodynamics and quantum mechanics. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the different states of matter and how they relate to the property of matter.
Solids are the most common type of matter and have a definite shape and volume. Their molecules are closely packed together, giving them a rigid structure. The molecules of liquids, on the other hand, are loosely packed and move around freely, meaning they take the shape of their container. Gases are composed of molecules that are far apart and can move in any direction.
Plasma is a fourth state of matter where matter is composed of electrically charged ions and electrons. This state of matter can be found in stars, lightning, and fluorescent lighting. Bose-Einstein condensates are a form of matter that exists at extremely cold temperatures where the atoms lose their individual properties and behave like a single entity. Quark-gluon plasmas are a type of matter that is composed of quarks and gluons and is found in the cores of neutron stars.
Each state of matter has unique properties that can be used to investigate the nature of matter and its various properties. For instance, the laws of thermodynamics can be used to study the energy states of solids, liquids, and gases. By studying the different states of matter, scientists can better understand how matter behaves and how it can be manipulated.
Classification of Matter
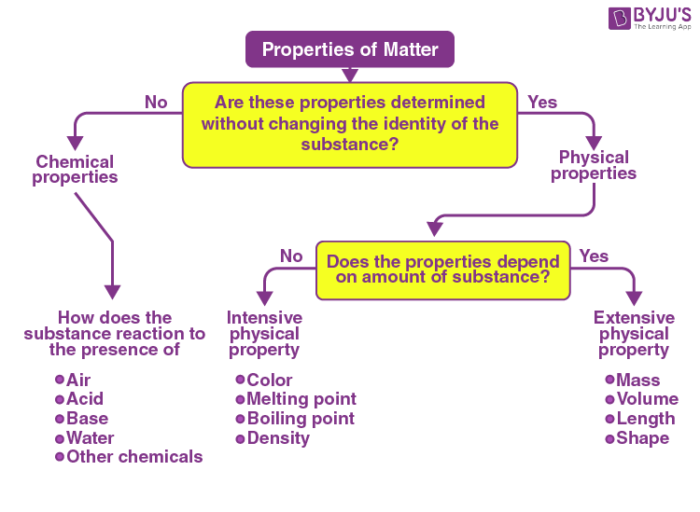
Matter is the basic substance that makes up our universe and can take many forms. It can exist as a solid, liquid, gas, or plasma and can be classified by its properties. Property of matter is the characteristics of matter that enable us to distinguish one type of matter from another. These properties include physical and chemical characteristics that allow us to identify the type of matter and how it behaves in various environments. Physical properties of matter, such as colour, density, and shape, can be observed without changing the type of matter. Chemical properties, such as reactivity with other substances, can only be determined by changing the type of matter. In this article, we will explore what is the property of matter, how it is classified, and how it affects our everyday lives.

Physical Properties of Matter
Matter is composed of atoms and molecules, and physical properties of matter are those that can be observed or measured without changing the composition of the substance. These are the properties that allow us to identify one material from another. Some of the most common physical properties of matter are mass, volume, density, state of matter, color, odor, and boiling point. Mass is the amount of matter contained in an object; volume is the amount of space that an object occupies; and density is the amount of mass per unit of volume. The state of matter refers to the form in which the material exists—solid, liquid, or gas. Color, odor, and boiling point are all physical properties that allow us to identify and differentiate between materials.
The physical properties of matter can be used to determine the composition of a substance and to identify the material. By understanding the physical properties of matter, scientists can use this knowledge to develop materials with specific properties to suit a particular application. For example, researchers can create materials that are lightweight but strong, or materials that are heat resistant for use in extreme temperatures. Thus, the physical properties of matter are essential to the development of new materials.
Chemical Properties of Matter
In chemistry, the physical and chemical properties of matter are closely related to its structure. The property of matter refers to its characteristics, such as its color, texture, and hardness. However, the chemical properties of matter are the ones that determine its reactivity with other substances. These properties, such as flammability, reactivity, and toxicity, all determine how matter interacts with other chemicals.
The chemical properties of matter are determined by its molecular structure. The bonds between atoms give rise to the various properties of matter, such as solubility and boiling point. The chemical properties of matter also depend on the type of elements it contains. For instance, the reactivity of an element such as sodium is very different from that of an element such as hydrogen.
The chemical properties of matter are also affected by its temperature and pressure. For instance, at higher temperatures, matter can be more reactive and can undergo chemical changes more easily. At lower temperatures, the reactivity of matter decreases, and it becomes more stable. Pressure also affects the chemical properties of matter; as pressure increases, so does the reactivity of matter.
Understanding the chemical properties of matter is essential for developing new materials and products. By studying the chemical properties of a specific material, scientists can determine how it will react with other substances and how it can be used in various applications. It is also important for safety, as knowing the chemical properties of a substance can help determine whether it is safe to handle.
Applications of Properties of Matter
The physical properties of matter are essential for understanding its behaviour in the real world. Matter can be studied in a variety of ways, from the macroscopic scale to the microscopic scale. On a macroscopic scale, the physical properties of matter can be used to describe its physical appearance, such as its shape, size, colour, and texture. On a microscopic scale, the physical properties of matter allow us to understand its internal structure and behaviour, including how it interacts with other particles.
The properties of matter are also important for understanding its applications in various fields. For instance, in the field of engineering, the properties of matter are used for designing materials to be used in structures, machines, and other products. In the field of chemistry, the properties of matter can be used to develop new materials, understand chemical reactions, and design new drugs and medicines. In the field of physics, the properties of matter allow us to understand various physical phenomena, such as the laws of motion, thermodynamics, and electromagnetism.
The properties of matter also have a wide range of uses in everyday life. For example, the properties of matter determine the strength of different materials, which can be used to build strong structures, such as bridges and buildings. The properties of matter also determine the properties of various substances, such as their melting point and boiling point, which can be used to control the temperature of our environment.
In conclusion, the properties of matter play an essential role in many scientific fields and everyday life. By understanding the properties of matter, we can learn how to design materials, understand chemical reactions, and control our environment.
FAQs About the What Is Property Of Matter?
Q1. What is the definition of property of matter?
A1. Property of matter is a characteristic of a substance or material that can be observed without changing the identity of the material. These properties may include physical, chemical, and other characteristics.
Q2. What are some examples of properties of matter?
A2. Some examples of properties of matter include mass, volume, density, state of matter, melting point, boiling point, electrical conductivity, and chemical reactivity.
Q3. How can I measure the properties of matter?
A3. The properties of matter can be measured using a variety of tools and techniques, such as calipers, scales, thermometers, and microscopes. Additionally, chemical tests can be performed to measure the reactivity of materials.
Conclusion
In conclusion, matter is an essential part of our universe and its properties are essential for us to understand and use in our everyday lives. Matter has a variety of properties that govern its interactions with other matter and its behavior under different conditions. These properties include mass, volume, density, and the ability to conduct or resist heat and electricity. By understanding these properties, we can better understand the world around us and the physical laws that govern it.