What Is Link Speed In WiFi?
Link speed is the measure of how fast data can be transferred between two devices on a wireless network. It is also known as data rate, or simply as the speed of a WiFi connection. Link speed is expressed as megabits per second (Mbps) or kilobits per second (kbps). The higher the number, the faster the connection. The link speed of a WiFi connection is determined by the router, the device being connected to, and the environment around the router. The speed of a WiFi connection can be affected by a number of factors, such as the distance between the router and the device, the presence of obstructions, and the number of users connected to the same network.
Definition of Link Speed
Link speed is an important element of any wireless network. It is the measure of how quickly data is transferred from one point to another. This is determined by the size of the data packet, as well as the amount of time it takes for the packet to be sent and received. Link speed can be configured manually or automatically, depending on the wireless network.
Link speed is expressed in terms of bits per second (bps) or megabits per second (Mbps). The higher the link speed, the faster the data transfer rate. In a home or office environment, it is important to have a high-speed connection to maximize internet access.
It is also important to note that link speed can be affected by a variety of other factors, including physical distance from the router, the type of network protocol used, and the number of other users connected to the same network. In order to maximize the speed of your connection, it is important to optimize your network settings and choose the right router for your needs.
Link speed is an essential part of any wireless network and is used to measure how quickly data is transferred. Knowing how to configure and optimize your link speed can help you get the most out of your internet connection.
Factors Impacting Link Speed
WiFi link speed is an important factor to consider when setting up a wireless network. It is the rate at which data is transferred between two devices connected via a wireless connection. It is affected by many factors such as distance, signal interference, router configuration, and hardware capabilities.
The distance between the two devices connected via WiFi is one of the main factors impacting link speed. The further away the devices are, the weaker the signal and the slower the speed. Additionally, signal interference from other electronic devices can also cause a decrease in link speed. To improve the signal quality and link speed, make sure your router is placed away from any other electronic devices.
Another factor that can affect link speed is the router configuration. Routers are typically set to operate at a certain speed, and this speed may not be optimal for your network. To get the best performance, you should configure your router to use the highest speed possible. Additionally, the hardware capabilities of the devices can also impact the link speed. Older devices may not be able to achieve the same speeds as newer devices, and if one of the devices in the connection is not capable of the highest speed, the link speed will be limited.
By understanding the factors that impact link speed, you can optimize your wireless network to get the best performance possible.
Measuring and Calculating Link Speed
Link speed is a vital element of a wireless network’s performance. Link speed, also known as data rate or transfer rate, is the speed at which data is transmitted between two points on a network. It is calculated by measuring the number of bits or bytes per second that are transmitted. This is important for ensuring a smooth and reliable connection, as well as for determining the maximum capacity of a given network.
When it comes to measuring and calculating link speed, there are several factors to consider. First, the type of connection – such as Wi-Fi, LTE, or 5G – will determine the speed of the link. Additionally, the distance between the two points and the number of devices connected to the network can affect the speed. Other factors, such as the amount of interference and the type of antenna used, can also play a role.
For optimal performance, it is important to properly monitor and adjust the link speed. This can be done by using various tools, such as a site survey or a speed test. This will help to determine the best settings for the network, as well as identify any potential issues that may be impacting performance. By doing this, users can ensure they are getting the most out of their connection.
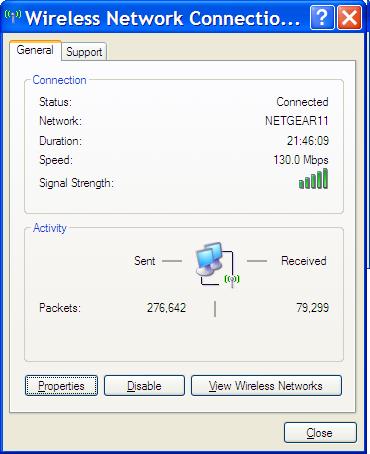
Common Link Speeds in Home and Business Networks
Wireless link speed is an important factor when setting up a home or business network. Link speed, also known as data rate, is the speed at which data moves over a wireless connection. Link speed is measured in megabits per second (Mbps), which is a measure of the amount of data that can be transferred in a given second. In today’s digital world, having a fast and reliable network connection is essential for both home and business users.
When it comes to home networks, most users are accustomed to seeing a maximum link speed of around 150 Mbps. This is the typical link speed provided by most consumer grade routers and is ideal for basic internet browsing, streaming music and video, and playing online games.
Business networks, on the other hand, require much faster link speeds. For example, many businesses are now using wireless networks with link speeds of up to 1 Gbps (1000 Mbps). This is much faster than a typical consumer-grade router and is ideal for tasks such as accessing large files, streaming high-definition video, and making VoIP calls.
It’s also important to note that link speed is not the only factor when setting up a wireless network. Other factors such as signal strength and latency can also affect the performance of a wireless network. So, it’s important to make sure that your wireless network is designed to meet the needs of your users.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Faster Link Speeds
WiFi link speeds are an important factor when it comes to optimizing your home network. Connecting your devices wirelessly is becoming increasingly popular, but the speed of the connection is essential for a smooth user experience. There are many benefits and drawbacks of faster link speeds, and understanding them is key to selecting the best option for your network.
The most obvious benefit of faster link speeds is increased data transfer rates. Faster speeds mean that data can be transferred faster, allowing for quicker downloads, streaming, and other online activities. Additionally, faster link speeds can help reduce interference from other wireless devices, as the signal can be sent and received faster.
On the other hand, faster link speeds can also be a detriment to your network. Faster speeds require more energy, which can lead to shorter battery life on mobile devices. Additionally, faster speeds can lead to an increase in latency, as the signal needs to travel at a faster rate. This can lead to choppy streaming and laggy online gaming.
Overall, faster link speeds may not be the right choice for every network. It is important to understand both the benefits and drawbacks of the technology before making a decision. With the right knowledge and preparation, you can ensure that you choose the right WiFi link speed for your needs.
How to Increase Link Speed in WiFi Networks
Having a good internet connection is essential for anyone, especially in our digital age. But what about link speed in WiFi networks? Link speed is the amount of data that can be transferred between two devices over a network connection, such as your router and your computer. It is important to have fast link speeds in order to ensure your internet connection is running at its best, and to avoid slowdowns and disruptions. Many factors can affect your link speed, but it is possible to improve it by following a few simple tips.
Firstly, routers come with different levels of power, so it is important to select the right one for your home. You should also consider the number of devices that will be connected to the network and the amount of data that will be transferred. Additionally, make sure to keep your router’s firmware up to date to ensure the best connection speeds.
You can also increase link speed by optimizing your WiFi network. This includes setting up the right channel, adjusting the power levels, and using the right antennas. Additionally, ensuring that your router is placed in the right position can make a big difference in signal strength and link speeds.
Lastly, if you are serious about optimizing your WiFi network, there are a few more advanced techniques you can try, such as using a range extender or a dedicated WiFi access point. These can help to provide a more reliable connection and a better link speed.
In conclusion, link speed in WiFi networks is an important factor to consider when it comes to ensuring a good internet connection. By following the tips above, you can improve your link speed and get the most out of your internet connection.
FAQs About the What Is Link Speed In WiFi?
1. What is the difference between link speed and data transfer rate in WiFi?
Link speed is a measure of how quickly data is transferred over a wireless network, while data transfer rate is the actual speed of the data transfer. The link speed is typically faster than the data transfer rate due to various factors, such as the number of users or devices connected to the network, the distance between the devices, and the type of WiFi technology used.
2. What is a good WiFi link speed?
The ideal link speed for a WiFi connection depends on the type of activities you plan to do on the network. For basic web browsing, a link speed of at least 54 Mbps is recommended. For streaming video or gaming, a link speed of at least 250 Mbps is recommended.
3. Can I increase my WiFi link speed?
Yes, you can. Depending on your router, you may be able to increase the link speed by changing the channel or antenna settings. You can also try using a WiFi extender or booster to extend the range and improve the signal.
Conclusion
In conclusion, link speed is an important factor when considering a WiFi network. Link speed is the measure of data transmission rate over a wireless connection, and it can significantly affect the performance of the WiFi network. While higher link speeds provide faster internet speeds, lower link speeds may be ideal for certain applications. Ultimately, choosing the right link speed for a particular WiFi network depends on the user’s needs and the type of applications that will be used.