What Is Industry 4.0 Also Called?
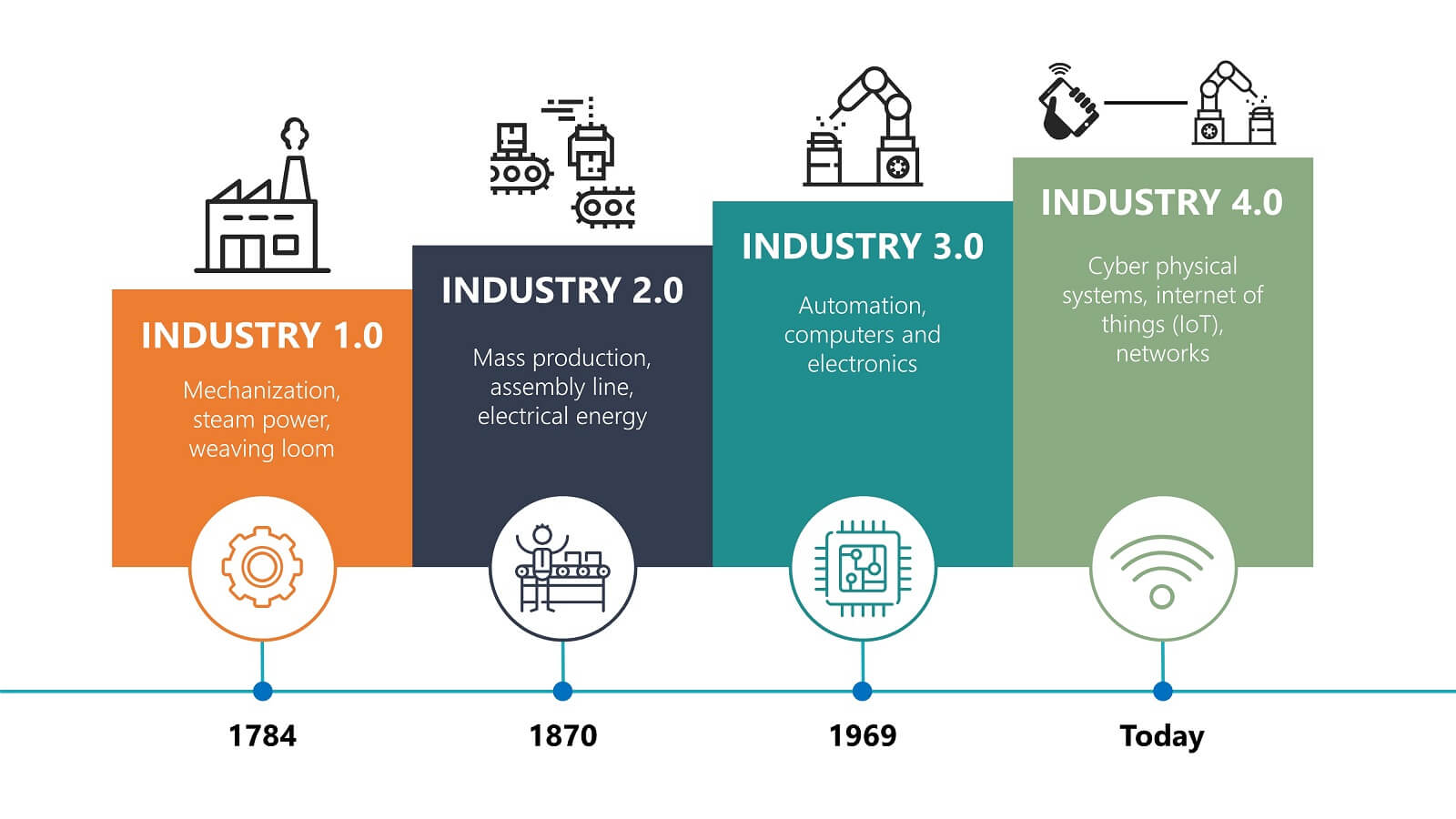
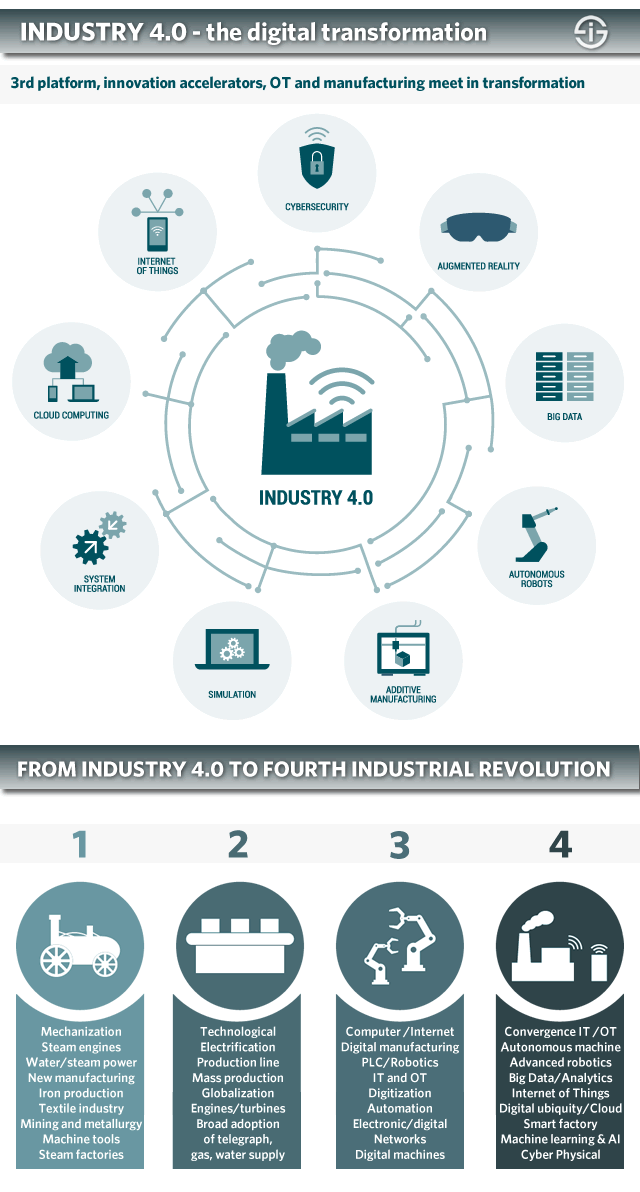
Industry 4.0, sometimes referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is a term used to describe the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. This includes the use of cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things, cloud computing and cognitive computing. Industry 4.0 creates what has been called a “smart factory,” in which a cyber system monitors physical processes, creates a virtual copy of the physical world and makes decentralized decisions. The goal of Industry 4.0 is to create an environment in which machines and humans can work together to create smarter, more efficient processes.
Overview of Industry 4
.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is a term used to describe the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It involves the integration of advanced digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), with traditional manufacturing techniques. In other words, it is the use of smart devices and technology to create an interconnected industrial ecosystem. Industry 4.0 is characterized by improved communication between machines and humans, increased efficiency of production processes, and improved customer service. As a result, it has revolutionized the way companies operate and is transforming the manufacturing industry.
Industry 4.0 encompasses a variety of technologies, including robotics, augmented reality, cloud computing, and machine learning. These technologies enable machines to process and analyze data quickly, allowing for more efficient production processes. They also enable companies to increase their customer service capabilities, such as providing personalized experiences. Additionally, these technologies enable companies to reduce costs and increase profits.
The potential of Industry 4.0 is immense. It has the potential to revolutionize the way companies operate and create new opportunities for businesses. By leveraging the power of Industry 4.0 technologies, companies can maximize their efficiency and reduce costs while still providing quality products and services. Ultimately, Industry 4.0 promises to revolutionize the manufacturing industry and create a better future for businesses around the world.
History and Development of Industry 4
.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is a term coined in 2011 to describe the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It is the culmination of multiple technological revolutions that have brought us from manual labor to highly complex and automated systems. By utilizing a combination of modern information technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, robotics, and the Internet of Things, Industry 4.0 is ushering in a new era of industrialization.
Industry 4.0 was first conceived by German Chancellor Angela Merkel in 2011 and has since been embraced by governments around the world. The main goal of the initiative is to create a fully automated and connected industrial ecosystem where machines communicate with each other and with human operators. This will enable factories to become more efficient, reduce production costs, and improve the quality of products.
In the years since its inception, Industry 4.0 has continued to grow and evolve. New technologies such as additive manufacturing, 3D printing, and Augmented Reality have been added to the mix, and the use of big data and predictive analytics has enabled manufacturers to make better business decisions. Furthermore, the implementation of Industry 4.0 has opened up new opportunities for small businesses to compete in global markets.
Overall, the Fourth Industrial Revolution has the potential to revolutionize the way we work, the way we produce goods, and the way we interact with the world around us. With the right policies and investments, it could also lead to a more equitable and sustainable future for all.
Benefits of Industry 4
.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, is a term used to describe the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. By leveraging the Internet of Things, the industrial internet of things, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and other related technology, Industry 4.0 is allowing manufacturers to create smarter, more efficient factories and production lines.
The benefits of Industry 4.0 are far-reaching, from increased efficiency and productivity to enhanced safety and quality control. By utilizing the latest technologies, manufacturers can reduce production costs, improve product quality, and increase customer satisfaction. Automated processes can reduce human error and improve accuracy, while predictive analytics can help manufacturers identify potential problems before they arise. Additionally, Industry 4.0 technology can be used to create more efficient supply chains, enabling manufacturers to deliver goods and services faster and more cost-effectively.
Finally, Industry 4.0 technologies can be used to enable better customer service and market research. By gathering data from customers, manufacturers can better understand their needs and preferences, allowing them to create customized products and services that better meet those needs. By creating an interconnected network of smart machines, manufacturers can gain a better understanding of their customers and the market, helping them to drive growth and increase profitability.
Industry 4.0 is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry, and its benefits are far-reaching. From increased efficiency and productivity to enhanced safety and quality control, manufacturers are leveraging the latest technologies to create smarter, more efficient factories and production lines. With the right strategies in place, manufacturers can capitalize on the potential of Industry 4.0 to create a more profitable and sustainable future.
Challenges of Implementing Industry 4
.0
Industry 4.0, also termed as the fourth industrial revolution, is a term used to describe the convergence of digital and physical technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, Automation, Internet of Things (IoT), etc. It is a concept that aims to revolutionize the production processes of the industrial sector.
The implementation of Industry 4.0 is no easy task, however, and requires careful consideration and strategic planning. Companies must consider the implications of introducing new technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, Automation, etc. into their production process. Additionally, companies must assess the potential risks and rewards associated with implementing Industry 4.0, including the cost, availability of resources, and data security.
Another challenge associated with Industry 4.0 implementation is the integration of the new technologies with existing systems. To successfully implement Industry 4.0, companies must ensure that the new technologies are compatible and can communicate with existing systems. This requires detailed analysis and testing to ensure successful integration.
Finally, companies must also consider the impact that implementing Industry 4.0 may have on their workforce. With the introduction of automation and robotics, there is a potential for job losses or displacement. Companies must take measures to ensure that their workforce is adequately trained and reskilled to make the transition to Industry 4.0 smoother.
Overall, the implementation of Industry 4.0 is a complex and challenging process. Companies must carefully consider the implications of introducing new technologies, ensure successful integration with existing systems, and ensure that their workforce is adequately trained and reskilled. With a strategic plan and careful consideration, however, companies can successfully implement Industry 4.0 and reap the rewards that it offers.
Examples of Companies Implementing Industry 4
.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is a term used to describe the digital transformation of industries. It signifies the convergence of data-driven technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing, as well as advanced manufacturing processes such as 3D printing, robotics, and automated production. As this new era of industrialization becomes more widespread, it is important to look at how companies are implementing Industry 4.0.
For example, Volkswagen Group has incorporated Industry 4.0 technologies into its factories, which has improved production efficiency by up to 25%. The company has also implemented a range of automated processes, including automated inventory management, automated production lines, and predictive maintenance. Siemens has similarly implemented Industry 4.0 in its factories, utilizing AI to improve production and distribution processes. The company has also implemented a range of IoT-enabled devices that enable predictive maintenance and improved production.
Other companies are taking a more holistic approach to Industry 4.0. Amazon has implemented a range of data-driven technologies to improve supply chain efficiency, from automated warehouses and robots to the use of predictive analytics. Microsoft has also implemented Industry 4.0 technologies in its factories, leveraging AI to improve production processes.
As Industry 4.0 becomes more widespread, it is clear that the traditional ways of doing business are changing. Companies that want to stay competitive in the age of Industry 4.0 must embrace data-driven technologies and advanced manufacturing processes. By leveraging the power of Industry 4.0, companies can improve efficiency and stay ahead of the competition.
Future of Industry 4
.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, is a term used to describe the transformation of traditional manufacturing and industrial practices with modern, data-driven technology and automation. It is a collection of innovative technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), that are changing the way goods are manufactured and how services are delivered. Industry 4.0 has the potential to revolutionize the way businesses operate, leading to increased efficiency, improved productivity, and cost savings.
The future of Industry 4.0 looks bright. Companies that are able to leverage the power of Industry 4.0 technologies will be better positioned to succeed in the highly competitive global market. This could be done by investing in technologies that facilitate data-driven decision making, such as predictive analytics and machine learning. Additionally, companies should focus on optimizing processes through automation and digitalization to reduce costs and increase efficiency. Companies should also invest in upskilling their employees to ensure that they are able to effectively adapt to the changing landscape.
FAQs About the What Is Industry 4.0 Also Called?
Q1: What is Industry 4.0?
A1: Industry 4.0 is the term used to describe the fourth industrial revolution, a digital transformation of the manufacturing industry that leverages the power of the Internet of Things (IoT), automation, data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) to improve efficiency and productivity.
Q2: What are the benefits of Industry 4.0?
A2: The benefits of Industry 4.0 include increased efficiency, improved customer experience, faster product development, and lower costs. It also enables businesses to take advantage of the Internet of Things (IoT) and automated processes to reduce manual labor and increase innovation.
Q3: What is Industry 4.0 also called?
A3: Industry 4.0 is also known as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Smart Manufacturing, and the Industrial Internet.
Conclusion
Industry 4.0 is also referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, or the Smart Factory Revolution. This term refers to the increasing use of digital technologies, such as big data, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the internet of things, to create more efficient, automated, and connected production processes. This revolution is transforming manufacturing and industrial processes, leading to increased productivity, improved safety, and reduced costs.