What Is Faster Than 2.4 GHz?
2.4 GHz is a measure of frequency used to measure the speed of wireless communication, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, some forms of communication are faster than 2.4 GHz. For example, Wi-Fi 6, which operates at 6 GHz, is much faster than the 2.4 GHz frequency. Additionally, other forms of communication such as fiber optic networks can provide even faster speeds than Wi-Fi 6.
Overview of 2
.4 GHz
When it comes to wireless technology, 2.4 GHz has been the industry standard for some time. It is a widely used frequency that is found in many wireless devices such as routers, phones, tablets, and other electronic gadgets. With the advancement of technology, however, the need for faster speeds has become more apparent. As such, faster frequencies have been developed such as 5 GHz and even higher. But what is faster than 2.4 GHz?
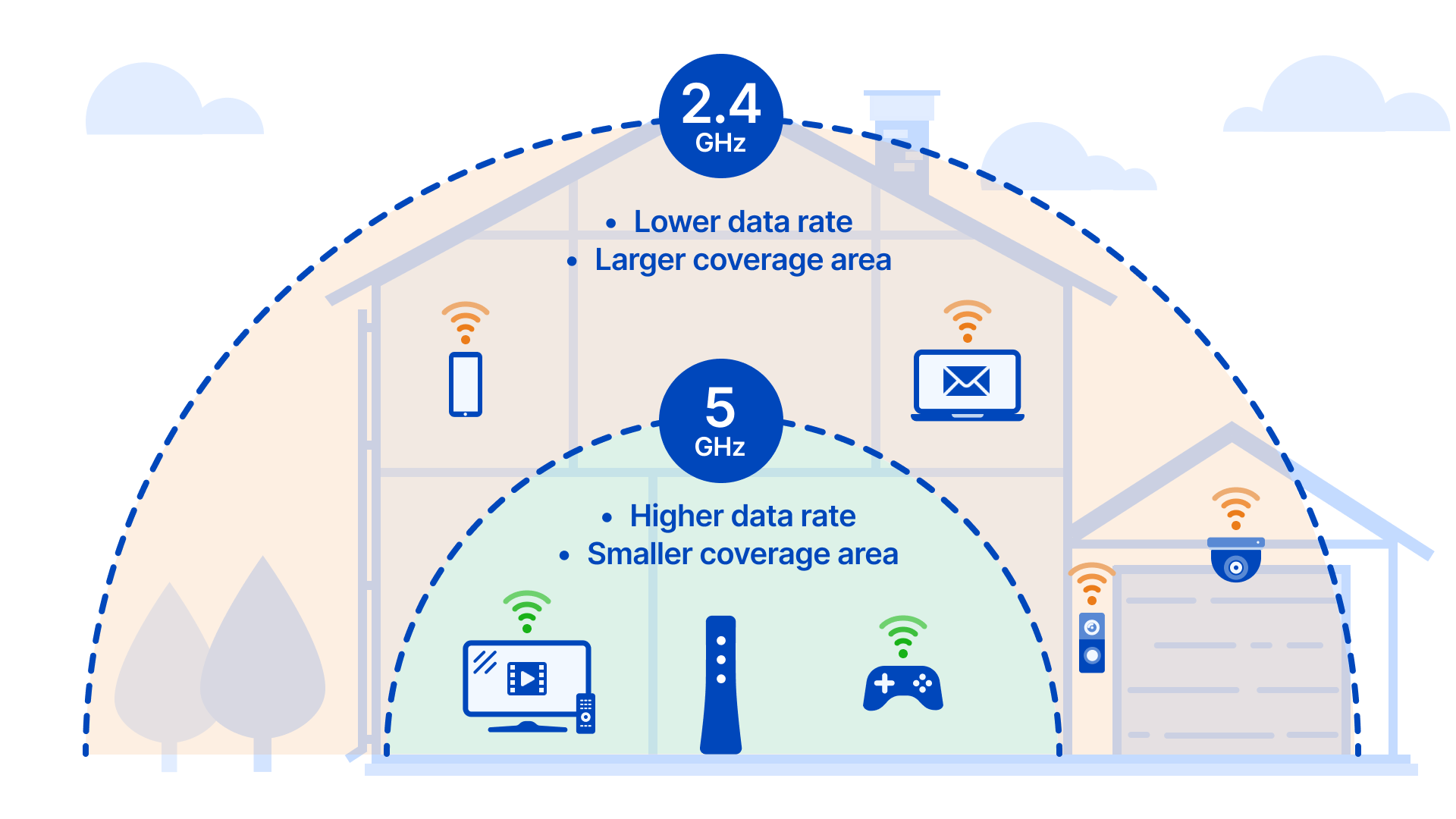
The most obvious answer to this question is 5 GHz. This frequency is capable of delivering speeds that are up to five times faster than 2.4 GHz. It is also more reliable and has less interference from other wireless devices. This makes it ideal for streaming media and online gaming. However, it does have a shorter range than 2.4 GHz and can be more expensive.
The next frequency that is faster than 2.4 GHz is the millimeter-wave frequency. This frequency is capable of delivering speeds up to 10 times faster than 2.4 GHz. It also has an even shorter range than 5 GHz and is much more expensive. This makes it a good choice for applications where speed is of the essence such as in the military and in data centers.
Finally, the highest frequency that is faster than 2.4 GHz is the terahertz frequency. This frequency is capable of delivering speeds up to 100 times faster than 2.4 GHz. It is also much more expensive and has an even shorter range than the millimeter-wave frequency. This makes it a good choice for applications requiring extremely high bandwidth such as in medical imaging.
In conclusion, there are several frequencies that are faster than 2.4 GHz. 5 GHz is the most widely used and is capable of delivering speeds up to five times faster than 2.4 GHz. The millimeter-wave frequency and terahertz frequency are capable of delivering speeds up to 10 times and 100 times faster than 2.4 GHz, respectively. All three of these frequencies are more expensive than 2.4 GHz and have shorter ranges. Ultimately, the choice of frequency will depend on the application and the user’s needs.
Benefits of 2
.4 GHz Networks
2.4 GHz networks are a common type of wireless network used in many homes and businesses. They offer a reliable connection and are usually sufficient for most basic needs. However, if you need more speed and reliability, you might want to consider upgrading to a faster network. In this article, we will explore the benefits of 2.4 GHz networks, and why they may be the perfect choice for your needs.
The biggest advantage of 2.4 GHz networks is their speed. They can provide speeds of up to 54 Mbps, which is more than enough for streaming videos and playing online games. Additionally, 2.4 GHz networks are compatible with a wide range of devices, making them a great choice for homes and businesses with multiple devices.
Another benefit of 2.4 GHz networks is their range. Since they use a lower frequency, they can cover a larger area than other types of networks. This makes them ideal for large homes and businesses with multiple rooms and floors.
Finally, 2.4 GHz networks are relatively inexpensive. While they may not be as fast as other types of networks, they are still an affordable option for those on a budget.
Overall, 2.4 GHz networks offer a reliable and affordable connection for both homes and businesses. With their higher speeds, wide compatibility, and long range, they are a great choice for those looking for an efficient and cost-effective network.
Disadvantages of 2
.4 GHz
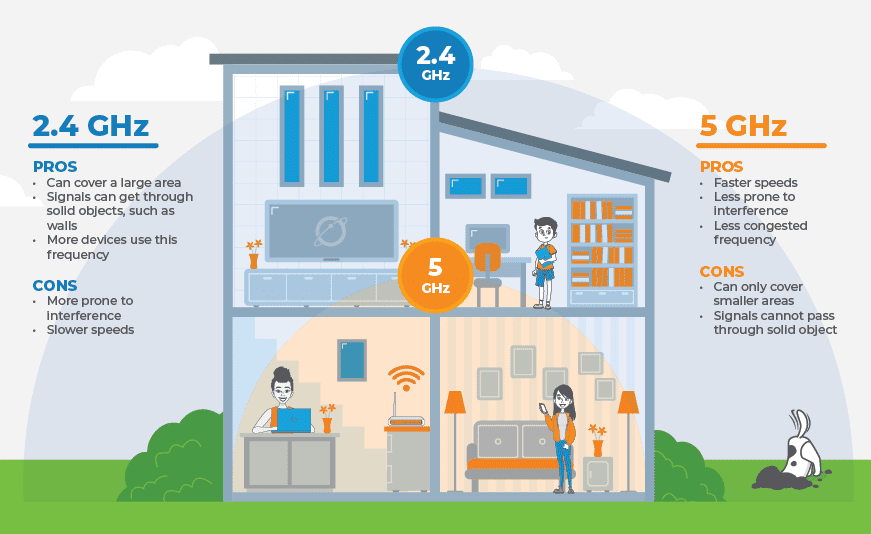
2.4 GHz is the frequency at which most wireless devices operate. This frequency is used by a variety of devices, including smartphones, tablets, and laptops. While 2.4 GHz has its advantages, it also has certain disadvantages. One of the main disadvantages of using 2.4 GHz is that it is prone to interference. 2.4 GHz networks can be affected by other devices operating on the same frequency, such as microwaves, Bluetooth, and other wireless networks. This can cause slowdown or even complete interruption of your connection. Furthermore, due to the high number of devices operating on 2.4 GHz, there is a limited number of available channels, which can cause congestion and slow down your connection speed. Additionally, the range of 2.4 GHz is lower than other frequencies, which results in a weaker signal over larger distances.
Overall, 2.4 GHz is a convenient and widely used frequency which has its advantages. However, due to its susceptibility to interference, limited available channels, and lower range, it is not the fastest frequency available. To get faster speeds, you might want to consider using 5 GHz or a wired connection.
Alternatives to 2
.4 GHz
It’s no secret that 2.4 GHz is a popular frequency for wireless networks, but did you know that there are faster alternatives out there?
For users seeking more speed, Wi-Fi 6E is the most recent development in wireless technology. With Wi-Fi 6E, users can access the 6 GHz band, which offers faster speeds, lower latency, and less interference than the 2.4 GHz band. This is because the 6 GHz band is much wider, meaning that it can carry more data than the traditional 2.4 GHz band.
For users who are looking for even faster speeds, there is also the 5 GHz band. This frequency is capable of delivering speeds of up to 1.3 Gbps, which is significantly faster than the 2.4 GHz band. The downside of the 5 GHz band is that it has a much shorter range, so users will need to be in close proximity to a router in order to get the best speeds.
Finally, there is the 10 GHz band. This band is not widely used, but it is capable of delivering speeds of up to 10 Gbps. The downside of the 10 GHz band is that it is more expensive to implement, and is not as widely available as the other alternatives.
No matter what speed you are looking for, there are alternatives to the traditional 2.4 GHz band that can offer faster speeds and better performance. Whether it’s Wi-Fi 6E, the 5 GHz band, or the 10 GHz band, you can find a wireless solution that meets your needs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Wi-Fi Frequency
When it comes to wireless networking, choosing the right Wi-Fi frequency is an important decision. With a variety of frequencies available, each offering their own advantages and disadvantages, selecting the most suitable one for your needs can seem daunting. To make the right decision, it is important to understand the basics of Wi-Fi frequency and the impact of 2.4 GHz frequency.
2.4 GHz is the most popular frequency for consumer wireless networking and is often the default frequency. Its popularity is due to its long-range coverage and the ability to penetrate obstacles such as walls and furniture. However, 2.4 GHz is also prone to interference from other wireless devices that operate within the same frequency range. Additionally, 2.4 GHz has a maximum bandwidth of 150 Mbps, making it unsuitable for activities that require high-speed data transfers.
Fortunately, there are other options. 5 GHz is a newer frequency that offers significantly higher bandwidths and is less prone to interference from other wireless devices. While 5 GHz is typically faster than 2.4 GHz, its shorter range means it may not be suitable for large homes or offices. Additionally, 5 GHz is more easily blocked by physical obstacles such as walls and furniture.
When selecting a Wi-Fi frequency, it is important to consider the environment and the activities that will be done over the network. For activities that require high data transfer speeds, such as streaming media or large file transfers, 5 GHz is the better choice. For large homes or offices, 2.4 GHz is the more practical choice due to its long-range coverage. Consider the pros and cons of each frequency and choose the one that is best suited for your needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when it comes to speed, 2.4 GHz is considered to be the standard for wireless networks. However, there are some technologies that offer faster speeds, such as 5 GHz networks, which offer up to four times more speed than 2.4 GHz networks and are often better suited for streaming media. Other technologies, such as Wi-Fi 6 and the 802.11ax standard, can offer even faster speeds of up to 10 Gbps, making them ideal for gaming and other high-bandwidth applications. Ultimately, the right technology for you will depend on your needs and your budget.
FAQs About the What Is Faster Than 2.4 GHz?
Q1: What is faster than 2.4 GHz?
A1: The available Wi-Fi frequencies range from 2.4 GHz to 5 GHz, with 5 GHz being the faster of the two.
Q2: How does 5 GHz compare to 2.4 GHz in terms of speed?
A2: The 5GHz frequency is typically faster than the 2.4GHz frequency, offering more bandwidth and less interference from other devices.
Q3: What devices work with 5 GHz?
A3: Many newer devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops are capable of connecting to both 2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi networks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that there are a variety of technologies and processors that are faster than 2.4 GHz. These technologies include multi-core CPUs, 5G networks, and even quantum computing. However, as technology continues to evolve, it is likely that even faster speeds will continue to become available.