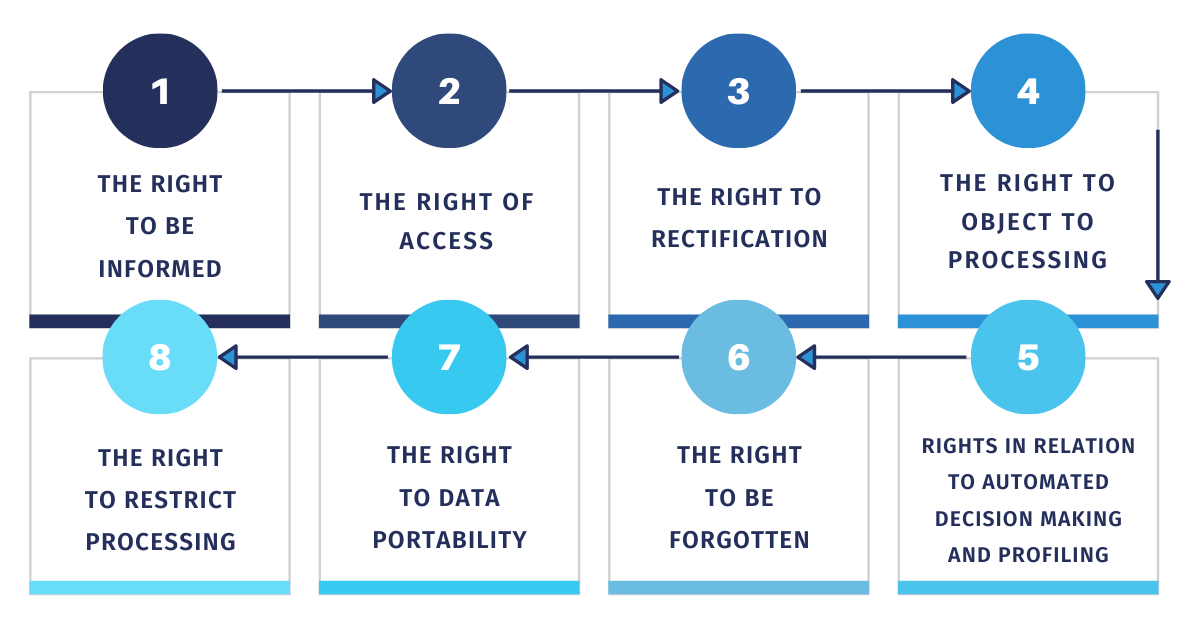
What Are The 7 Rights Of Data Privacy?
Data privacy is an important concept in today’s digital world. It is the right to control your own personal data and keep it confidential. The 7 Rights of Data Privacy are a set of principles and guidelines that aim to protect the privacy of individuals and organizations. They are established by the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). These seven rights include: the right to be informed; the right of access; the right of rectification; the right to erasure; the right to restrict processing; the right to data portability; and the right to object. Each of these rights plays a vital role in protecting personal data and giving individuals a sense of control over how their information is collected, stored, and used.
Definition of Data Privacy Rights
Data privacy rights are the legal and moral rights that individuals have to control the collection, use, and dissemination of personal information about themselves. These rights exist to protect individuals from the potential abuse of their information by organizations and governments. Data privacy rights are an essential part of any individual’s right to privacy, and it is important to be aware of them and what they mean. Data privacy rights give individuals the power to decide what information about them is collected, how it is used, and how it is shared with others. They provide assurance that any collected information will be kept secure and used responsibly. With data privacy rights, individuals can be confident that their information is being handled in a way that respects their privacy and safeguards their data.
Right to Access
Right to Access is a blog that provides readers with the latest news and information on the right to access public and private data. It offers in-depth analysis on the legal issues surrounding the right to access data, as well as insight into the implications of open data initiatives. The blog is a great resource for those interested in understanding more about the right to access data in the digital age. It provides a platform for discussing the ethical implications of the right to access data, as well as its potential use in business, government, and citizen empowerment. Right to Access is your one-stop resource for staying informed and up-to-date on the latest news and developments related to the right to access data.
Right to Rectification
Right to Rectification is the right of individuals to have inaccurate data concerning them rectified or corrected. This right is a cornerstone of the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). It applies to both the controller of the personal data (the person or organization that collects and processes it) and the processor (the person or organization that processes it on behalf of the controller). It gives individuals the right to have inaccurate or incomplete personal data rectified or added to, as well as the right to have any inaccurate or incomplete personal data blocked, erased or destroyed. This right is key to protecting the personal data of individuals and ensuring its accuracy and completeness.

Right to Erasure
The “Right to Erasure” is a fundamental right that allows individuals to request that their personal data be deleted from any company’s records. This right provides individuals with a greater level of control over their personal data and allows them to protect their privacy. As a business, it is important to comply with the Right to Erasure, as failure to do so can result in severe legal and financial consequences. The Right to Erasure is a powerful tool that allows individuals to take control of their personal data and ensure that it is not misused or abused. This right is essential to protecting the privacy of individuals and providing them with the peace of mind that their data is safe and secure.
Right to Withdraw Consent
The right to withdraw consent is a fundamental right that allows individuals to revoke or withdraw their permission for something. This can be applied to a variety of situations, such as data collection, health care decisions, and even the use of a service. When a person withdraws their consent, the organization, service provider, or individual they are dealing with must stop processing the data or providing the service. It’s important to remember that consent can be withdrawn at any time, so it’s important to make sure that all parties involved are aware of the right to withdraw consent. By providing individuals with the ability to revoke their consent, organizations can ensure that their customers and clients are in control of their data and their decisions.
Right to Object
The Right to Object is a fundamental human right that protects us from unfairness and discrimination. It is the right to challenge a decision made about you or another person, and is protected by the European Convention on Human Rights. This right is especially important in situations where people feel that their rights have been violated or they have been treated unfairly. It allows individuals to take a stand against injustices and fight for justice. This right is exercised in many different ways, such as filing a complaint, appealing a decision, or taking legal action. It is also important to remember that the Right to Object is not just a right to challenge decisions made by others, but also a right to express one’s opinion and make sure that their voice is heard.
Right to Restrict Processing
When it comes to personal data, right to restrict processing is a key part of your rights. It allows you to request that your data controller stops or restricts the processing of your personal data. This means that the controller must stop processing the data or only process it in certain ways, such as storing it or using it for limited purposes. You can exercise this right if you believe the data controller is processing your data unlawfully, or if you don’t want the data controller to process your personal data for marketing or other purposes. It is important to note that right to restrict processing does not have the same effect as right to erasure, so data controllers may still be able to keep your data in certain circumstances.
FAQs About the What Are The 7 Rights Of Data Privacy?
Q1: What are the 7 rights of data privacy?
A1: The 7 rights of data privacy are the right to be informed, the right of access, the right of rectification, the right to erasure, the right to restrict processing, the right to data portability, and the right to object.
Q2: How can I ensure my data privacy rights are being protected?
A2: You can ensure your data privacy rights are being protected by ensuring that any company or organization that you share personal data with has a secure data privacy policy in place, as well as strong security measures to protect your data from unauthorized access.
Q3: How can I know if a company or organization is compliant with data privacy law?
A3: You can check with the company or organization to find out if they are compliant with data privacy law. Additionally, you can check to see if the company or organization has been certified by a third-party organization such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Conclusion
Overall, the 7 rights of data privacy are important for any individual or company to be aware of. These rights protect the personal information of individuals by making sure that companies use their data responsibly and ethically. They also ensure that individuals have the right to access, delete, and control the way their information is used. These rights are essential for protecting the privacy of individuals and ensuring that data is not misused or exploited.