What Are The 6 Principles Of Insurance?
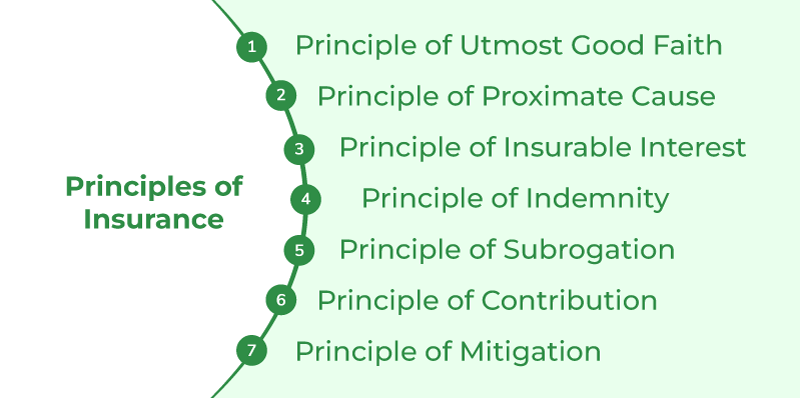
The 6 principles of insurance are commonly referred to as the bedrock of any insurance contract and provide the foundation for the insurance industry. These principles are the foundational beliefs and values that guide the industry in its practices and policies. They are utmost good faith, insurable interest, indemnity, contribution, subrogation, and loss minimization. These principles are essential for understanding how the insurance sector works and have been around since the 1800s. Understanding the 6 principles of insurance is integral for a proper understanding of the insurance industry.
Overview of Insurance Principles
Insurance is a form of risk management in which a person or entity pays a premium to an insurance company in order to be protected from certain types of losses, such as property damage, medical expenses, and more. Insurance is an important part of financial planning and is used to protect against potential losses due to unforeseen circumstances. Insurance is based on six principles that define the scope of coverage and the terms of the policy. These are Utmost Good Faith, Insurable Interest, Proximate Cause, Subrogation, Indemnity, and Contribution.
Utmost Good Faith is an insurance principle that requires the policyholder to provide honest and accurate information to the insurance company when purchasing a policy. Insurable Interest requires the policyholder to have a direct financial interest in the property or person being insured. Proximate Cause is the direct cause of the loss or damage. Subrogation allows the insurance company to pursue a third party for reimbursement. Indemnity requires the policyholder to be made whole after a loss, and Contribution requires policyholders to share losses in certain circumstances.
Understanding the basic principles of insurance is essential for making informed decisions about your insurance needs. Knowing how each principle works will help you make an educated decision about the type and amount of coverage that is best for you.
Principle of Utmost Good Faith
:
Insurance is a contract between two parties in which a policyholder pays an insurance company a premium in exchange for financial protection against potential losses. To ensure fairness and transparency, insurance is governed by six core principles. The first of these principles is the Principle of Utmost Good Faith, which is also known as the Principle of Uberrima Fides. It requires both the insurer and the policyholder to act in good faith toward each other. This means that the policyholder must provide accurate, up-to-date, and complete information about any potential risks to the insurer and must not knowingly conceal any relevant facts or information. The insurer, on the other hand, must provide complete and accurate information regarding the coverage and any exclusions and must not misrepresent the terms of the policy. The Principle of Utmost Good Faith is essential for the insurance contract to be valid and binding. It ensures that the insurer and the policyholder have a mutual understanding of the terms and conditions of the policy and creates an atmosphere of trust and fairness in the insurance relationship.
Principle of Insurable Interest
, Principle of Utmost Good Faith, Principle of Indemnity, Principle of Subrogation, Principle of Contribution, and Principle of Proximate Cause.
Insurance is an essential part of life as it helps us protect our assets, families, and belongings. It is important to understand the different principles of insurance to make sure you have the right coverage for your needs. The 6 principles of insurance are Principle of Insurable Interest, Principle of Utmost Good Faith, Principle of Indemnity, Principle of Subrogation, Principle of Contribution, and Principle of Proximate Cause.
The Principle of Insurable Interest states that an individual must have an interest in the object they are insuring. This means that the individual must suffer a financial loss if the object is damaged or destroyed. The Principle of Utmost Good Faith requires that the insurer and the insured be honest and truthful with each other during the insurance contract. The Principle of Indemnity states that the insured will be compensated for the loss but no more than the actual value of the property.
The Principle of Subrogation enables the insurer to recover the money paid to the insured from a third party who is responsible for the loss. The Principle of Contribution states that if two or more insurers are covering the same property, they will share the losses in proportion to their respective policies. Finally, the Principle of Proximate Cause requires that the loss must be the result of the covered peril in order for the insured to be compensated.
Understanding the 6 principles of insurance is essential for making sure you have the right coverage for your needs. Knowing the principles of insurance helps to ensure that you are protected and that you receive the compensation you are entitled to in the event of a loss.
Principle of Indemnity
:
Insurance is a contract between two parties, in which an insurer agrees to provide financial compensation to the insured in case of an event such as illness, accident, or death. Insurance is a safety net for individuals and businesses, providing them with financial protection if the worst were to happen. One of the most important principles of insurance is the principle of indemnity. This principle states that an insured person or organization should not be placed in a better financial position than they were prior to the insured event. In other words, the insurer pays out the exact amount to cover the insured’s losses and not more. This helps to prevent any kind of profiteering and ensures the insured person or organization is not incentivized to take risks they otherwise wouldn’t. The principle of indemnity is an integral part of insurance contracts and is enforced by all insurance providers. It helps to ensure fairness and transparency in insurance transactions.
Principle of Subrogation
The principle of subrogation is an important concept in the insurance industry. It states that if an insured person makes a claim due to a loss caused by a third party, the insurer is entitled to take over the rights of the insured and pursue the third party for recovery of the amount paid out to the insured. In other words, the insurer can “stand in the shoes” of the insured and take legal action to recover the costs of the claim. This principle allows insurers to reduce their overall losses by recovering some of the costs they have paid out to the insured. It is important to note that the principle of subrogation does not apply to all insurance policies. It can be limited by certain policy provisions and any applicable state laws. In addition, the insurer must be able to prove that the third party was responsible for the loss in order for the principle to be applied.
Principle of Contribution
, Principle of Insurable Interest, Principle of Indemnity, Principle of Subrogation, Principle of Utmost Good Faith, and Principle of Proximate Cause.
Insurance is a vital financial tool for individuals and businesses alike. In order to ensure that it can be used effectively it is important to understand the six core principles of insurance. These principles are Principle of Contribution, Principle of Insurable Interest, Principle of Indemnity, Principle of Subrogation, Principle of Utmost Good Faith, and Principle of Proximate Cause.
The Principle of Contribution states that in the event of a claim, multiple insurers are liable to contribute to the loss. This is especially important for large losses where multiple policies may be in place. The Principle of Insurable Interest is the legal requirement that the policyholder has a vested interest in the property being insured. The Principle of Indemnity states that the insured can be compensated for their loss, but not for a greater amount than their actual loss.
The Principle of Subrogation allows the insurer to take on the rights of the insured and seek reimbursement from a third party that has caused the loss. The Principle of Utmost Good Faith requires all parties involved in the insurance agreement to act honestly and in good faith to uphold the contract. Lastly, the Principle of Proximate Cause states that a claim must be based on a direct cause of loss that is covered under the policy.
Understanding these six principles of insurance is essential for individuals and businesses who are looking to maximize the effectiveness of their policies. With the right knowledge and understanding, individuals and businesses can ensure they have the protection they need.
Conclusion
Insurance is a vital tool for managing risk and ensuring financial security. It can help to protect both individuals and businesses from the potentially devastating effects of unexpected events. Although it can be complex, understanding the six basic principles of insurance can help to make the process simpler and more straightforward. These principles are the law of large numbers, utmost good faith, insurable interest, indemnity, subrogation and contribution. By familiarizing yourself with these key concepts, you can make more informed decisions about which insurance policies are right for you and your business.
FAQs About the What Are The 6 Principles Of Insurance?
Q1: What are the 6 principles of insurance?
A1: The 6 principles of insurance are insurable interest, utmost good faith, proximate cause, indemnity, subrogation, and contribution.
Q2: How does insurable interest apply to insurance?
A2: Insurable interest is the legal principle that states a Policyholder must have a financial interest in the insured item in order to be able to purchase an insurance policy.
Q3: What is the purpose of the principle of indemnity in insurance?
A3: The purpose of the principle of indemnity in insurance is to ensure that the Policyholder does not profit from an insurance claim. The intent is to put the Policyholder back into the same financial position they were in before the loss occurred.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the six principles of insurance are utmost good faith, insurable interest, indemnity, subrogation, contribution and loss minimization. These principles are the foundation of insurance policies and must be understood by the policyholder in order for them to make informed decisions about their insurance coverage. The principles help ensure that the insured and insurer are both treated fairly in the event of a claim.