What Are The 5 Principles Of Insurance?
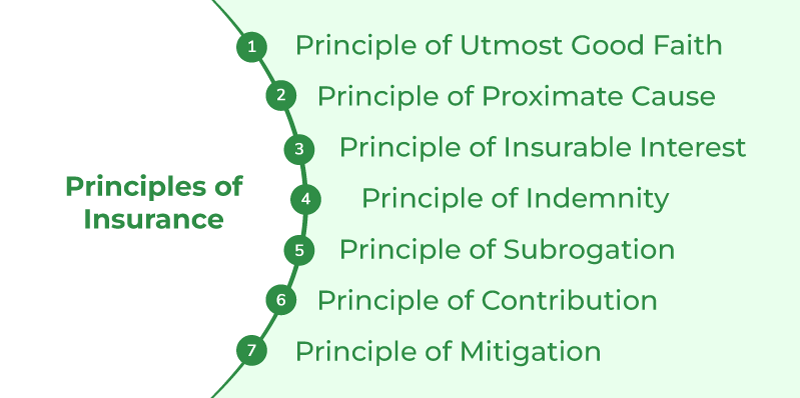
Insurance is a critical tool for helping individuals, families, and businesses manage risk and protect against losses that can arise from unexpected events. The 5 principles of insurance provide the foundation for insurance policies and the industry itself. These principles include indemnity, insurable interest, utmost good faith, contribution, and subrogation. Together, they empower insurers to adequately assess risk, set premiums, and protect policyholders.
Overview of Insurance Principles
Insurance is an important concept for businesses and individuals alike. It is a form of risk management that provides financial protection against unexpected losses. To help you understand how insurance works, it is important to understand the five fundamental principles of insurance. These principles are utmost good faith, insurable interest, indemnity, subrogation, and contribution.
The principle of utmost good faith requires that both the insurer and the insured be honest and forthcoming in their dealings. It is the insurer’s responsibility to provide an accurate assessment of the risk and to protect the insured’s interests. On the other hand, the insured must provide accurate information regarding the risks being insured.
The principle of insurable interest means that the insured must suffer a financial loss in the event of a claim. If the person does not stand to suffer a financial loss, then there is no insurable interest.
The principle of indemnity states that the insured should not profit from a claim. The aim is to restore the insured to the same financial position as before the loss occurred.
The principle of subrogation allows the insurer to pursue a third party in order to recover losses incurred by the insured. This principle is often used when the insured has been negligent in some way.
The principle of contribution states that if multiple insurance policies cover the same loss, the insurers must share the costs.
These five fundamental principles of insurance are essential for understanding how insurance works and how it can be used to protect individuals and businesses. It is important for businesses and individuals to understand these principles so that they can make informed decisions when purchasing insurance policies.
Principle of Utmost Good Faith
, Principle of Insurable Interest, Principle of Indemnity, Principle of Subrogation, and Principle of Contribution
Insurance is a contract between two parties, designed to protect against financial losses in the event of an unfortunate incident. To ensure fairness to all parties involved, insurance providers and payers must adhere to certain principles. The five most important principles of insurance are the Principle of Utmost Good Faith, Principle of Insurable Interest, Principle of Indemnity, Principle of Subrogation, and Principle of Contribution.
The Principle of Utmost Good Faith requires the insurance provider to be honest and transparent with the insured party about all of the terms and conditions of the policy. The Principle of Insurable Interest means that the insured party must have a financial stake in the property or person that they are insuring. The Principle of Indemnity states that the insured party should not gain or lose from the insurance policy, instead, they should be restored to the same financial position as they had prior to the incident. The Principle of Subrogation allows the insurance provider to take over the legal rights of the insured party and recover damages from a third party. Lastly, the Principle of Contribution ensures that each insurer pays their share of a claim if multiple policies are involved.
By understanding and adhering to these five principles, insurance providers and payers can ensure that all parties involved in the insurance contract are treated fairly.
Principle of Insurable Interest
, Principle of Utmost Good Faith, Principle of Indemnity, Principle of Subrogation, Principle of Contribution
Insurance is a complex yet essential financial tool that plays a crucial role in our modern lives. Insurance helps us protect ourselves from unexpected losses and provides us with financial security. Insurance works on five key principles that must be understood in order to maximize its benefits. These five principles are the Principle of Insurable Interest, Principle of Utmost Good Faith, Principle of Indemnity, Principle of Subrogation, and Principle of Contribution.
The Principle of Insurable Interest states that an individual must have a legal or financial interest in the property or person to be insured. This means you cannot purchase insurance policies on someone just to be charitable. The Principle of Utmost Good Faith requires that both the insurer and the insured be honest with each other in all their dealings. The Principle of Indemnity states that the insured will be compensated only for the actual loss suffered, less any deductible. The Principle of Subrogation allows the insured party to transfer their rights of recovery to the insurer. Lastly, the Principle of Contribution requires that the insured pay only their proportion of the loss, regardless of the amount of insurance coverage purchased.
These five principles are at the core of insurance and are vital for understanding how it works. Knowing and understanding these principles will help you make informed decisions about the insurance policies you purchase, and help you utilize the most out of insurance.

Principle of Indemnity
, Principle of Insurable Interest, Principle of Utmost Good Faith, Principle of Causa Proxima, Principle of Contribution.
Insurance is an important part of our lives, but do you know the five principles of insurance? Understanding the five principles of insurance can help you make more informed decisions when choosing the right insurance policy or plan for you. The five principles of insurance are: Principle of Indemnity, Principle of Insurable Interest, Principle of Utmost Good Faith, Principle of Causa Proxima, and Principle of Contribution.
The Principle of Indemnity states that the insured should not be placed in a better financial position than before the loss. This means that the insured should be entitled to only the amount of money required to restore them to the position they were in before the loss occurred.
The Principle of Insurable Interest states that the policyholder must have an insurable interest in the property or life covered by the insurance policy. This means that the policyholder must have a real financial loss if the property or person is damaged or destroyed.
The Principle of Utmost Good Faith requires that both parties in an insurance transaction are honest with each other. This means that the policyholder should provide complete and accurate information to the insurer, while the insurer should be transparent about the terms of the policy.
The Principle of Causa Proxima states that the closest cause of the loss should be identified to determine the amount of compensation to be paid. This means that the insurer should only cover losses that are a direct result of the peril covered by the policy.
The Principle of Contribution requires that all insurance policies covering the same risk should contribute to the payment of a claim. This means that if multiple policies cover the same risk, each policy will be responsible for paying a portion of the claim.
Understanding these five principles of insurance is essential for making informed decisions when selecting an insurance policy. Knowing the principles can help you determine what type of policy you need and how much coverage you should have. Being informed about the principles can help you make sure you are getting the most out of your insurance policy.
Principle of Subrogation
Insurance is based on five main principles, which are essential for understanding how insurance works. One of these principles is Subrogation, which allows an insurance company to take action on behalf of the insured in the event of a claim. This principle is based on the concept of substitution, whereby the insurer stands in the place of the insured and takes legal action against a third party who is responsible for the loss. In this way, the insurance company can recoup costs and damages incurred by the insured. This principle also gives the insurer the right to decide how to pursue a claim, such as through negotiations, arbitration, or litigation. Subrogation is a powerful tool to protect the insured and the insurer alike, but it must be used carefully and with the insured’s consent. Understanding this principle is key to making sure that insurance claims are handled appropriately and that the insured’s rights are respected.
Principle of Contribution
, Principle of Utmost Good Faith, Principle of Insurable Interest, Principle of Indemnity and Principle of Subrogation.
Insurance is a financial product that provides us with the security and protection we need against potential losses. It is a complicated subject, but understanding the five principles of insurance is a great start to becoming an educated consumer. These principles are the foundation of the insurance industry and are fundamental in understanding how insurance works.
The first principle is the Principle of Contribution, which states that each insurer contributes to the overall risk of the insurance portfolio. This means that each insurer will assume responsibility for a portion of the total risk.
The second principle is the Principle of Utmost Good Faith, which states that insurers and policyholders must act in an honest and transparent manner. This means that both parties must be honest and forthcoming about any information related to the policy.
The third principle is the Principle of Insurable Interest, which states that an individual must have a financial interest in the insured property or person in order to be eligible for insurance coverage. This means that an individual must have a financial stake in the property or person they are insuring.
The fourth principle is the Principle of Indemnity, which states that the insurer will only cover the amount of the loss. This means that if the insured property or person is damaged or destroyed, the insurer will only pay out the amount of the loss and not more.
Finally, the fifth principle is the Principle of Subrogation, which states that the insurer has the right to pursue a third-party for the cost of the claim. This means that if the insured property or person is damaged or destroyed due to the negligence of a third-party, the insurer can pursue the third-party for the cost of the claim.
Understanding these five principles of insurance is essential to being a knowledgeable and informed consumer. By understanding these principles, we can make smart and informed decisions when it comes to selecting an insurance policy that best fits our needs.
FAQs About the What Are The 5 Principles Of Insurance?
Q1. What Are The 5 Principles Of Insurance?
A1. The 5 principles of insurance are: Insurable Interest, Utmost Good Faith, Proximate Cause, Indemnity, and Subrogation.
Q2. What Is Insurable Interest?
A2. Insurable interest is a concept of common law that refers to the requirement that an individual or business must have a financial stake in the insured subject before they are eligible to purchase an insurance policy.
Q3. What Does Utmost Good Faith Mean?
A3. Utmost good faith is an insurance principle that states the insured and insurer must act honestly and in good faith when entering into a contract, and both parties must disclose all relevant information to each other.
Conclusion
The 5 principles of insurance are key concepts that help define the foundation of insurance. They are utmost good faith, insurable interest, indemnity, subrogation, and contribution. Each of these principles guide insurers and insured parties in understanding the scope of coverage provided by insurance policies and the obligations of each party. Insurance policies are inherently complex and these principles help to ensure that all parties understand their rights and responsibilities when it comes to insurance coverage.