What Are Organs?
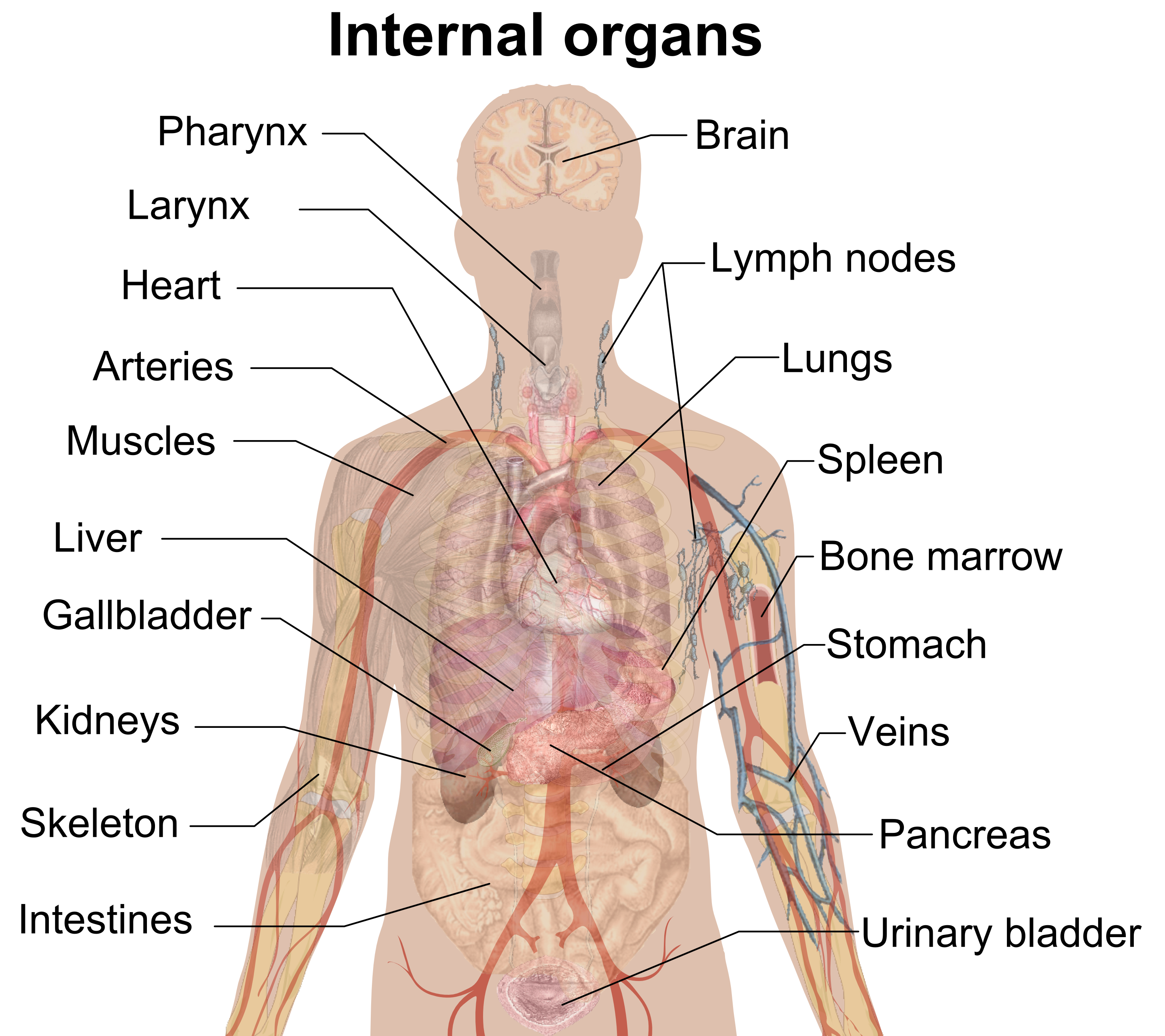
Organs are specialized structures in the human body that are responsible for performing specific functions. They are made up of tissues, cells, and other components that work together to perform one or more vital roles. Organs provide essential functions, such as digestion, respiration, and circulation, that keep the body running smoothly. They also help to protect the body from disease and injury. The major organs of the human body include the brain, heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, and intestines.
Definition of an Organ
An organ is a specialized structure within a living organism that performs particular functions. Organs are made up of tissues that work together to achieve a common goal. While organs vary in size and structure, each type is responsible for carrying out a specific set of tasks. The human body is made up of many different organs, including the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, and liver. These organs are essential for the body to function properly.
Each organ is composed of multiple types of cells that work together to carry out complex tasks. For example, the heart is made up of muscle cells, connective tissue cells, and nerve cells, all of which work together to pump blood throughout the body. Organs are also composed of various systems, such as the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, which are responsible for the body’s circulation and respiration.
While organs are essential for life, they can also be vulnerable to disease and injury. Diseases such as cancer can affect organs, and even the most minor injury can have serious consequences. Therefore, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and practice preventive care to prevent organ damage.
By understanding organ structure and function, we can better understand how the body works and how to keep it healthy. Knowing how organs work can help us recognize signs of disease and prevent injury. In short, organs play an essential role in keeping us alive and well.
Anatomical Classification of Organs
Organ systems are composed of a number of individual organs, each with its own unique structure and function. Organs are made of multiple types of tissues and are anatomically classified into four main categories. These categories are glands, hollow organs, muscles, and other organs.
Glands are organs composed of specialized cells that produce and secrete substances such as hormones, enzymes, or other materials. Examples of glands include the pancreas, salivary glands, and pituitary gland.
Hollow organs are organs that have a distinct lumen, or cavity, within them. Examples of hollow organs include the stomach, intestines, and urinary bladder.
Muscle organs are organs composed of muscle tissue and are responsible for body movements. Examples of muscle organs are the heart, diaphragm, and tongue.
Other organs are organs that do not fit into any of the other categories and are divided further into two subcategories. These subcategories are the dermis and appendages. The dermis is composed of skin, nails, hair, and sweat glands, while appendages are organs such as the eyes, ears, and nose.
In conclusion, organs are anatomically classified into four main categories, which are glands, hollow organs, muscles, and other organs. These four categories are further divided into subcategories, each with its own unique structure and function. Understanding the anatomical classification of organs is important for the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions.
Common Organs in the Human Body
Organs are the structural components of a living organism that allow it to function. For humans, organs work together as a system to keep us alive and healthy. Common organs in the human body include the brain, heart, lungs, liver, and kidneys. All of these organs are vital for life, as they perform important functions that maintain our health.
The brain is responsible for controlling our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. It is also responsible for our memory, language, and motor functions. The heart pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing waste. The lungs take in oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism. The liver is responsible for metabolizing nutrients, detoxifying the body, and producing bile. Finally, the kidneys filter waste and toxins from the bloodstream, helping to maintain fluid balance and blood pressure in the body.
These organs are essential for life, and any damage or disease to these organs can lead to serious health complications. It is important to take care of your body by eating healthy, exercising, and avoiding harmful substances. Taking care of your organs can help to ensure a healthy and long life.
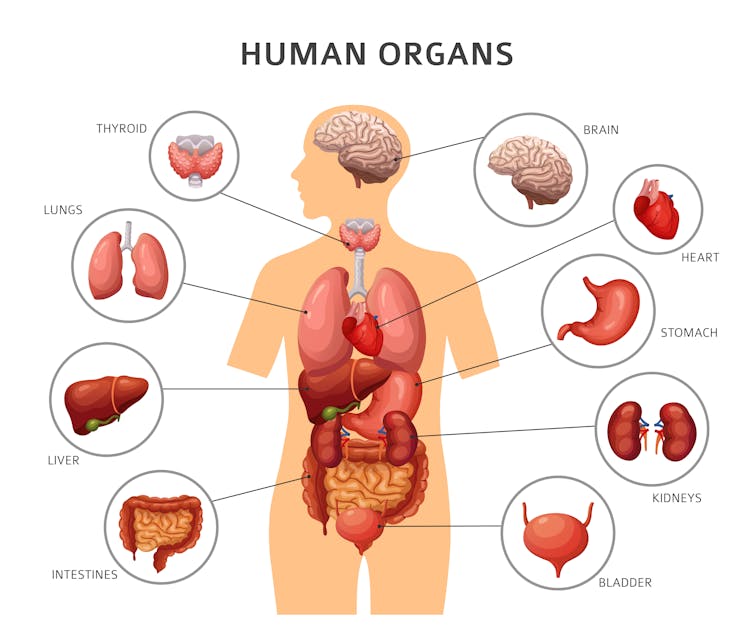
Functions of Organs
Our body is made up of numerous organs that all have their own unique functions. Organs are collections of tissues that are grouped together to perform specific tasks. They are responsible for carrying out vital body functions, such as digestion, respiration, circulation, and reproduction.
Organs vary in size and complexity, depending on their purpose. For example, the liver is a large organ that performs many important functions, while the small intestine is a complex organ that plays a vital role in digestion.
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, while the lungs are responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The kidneys and the bladder are responsible for the body’s waste removal process. The brain is the organ responsible for coordinating the body’s activities, while the eyes, ears, and nose are responsible for providing the body with sensory information.
Organs are also responsible for the production of hormones, which regulate the body’s growth and development. The pancreas is an organ that produces hormones and enzymes that help to digest food, while the thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism.
The organs of the body work together to keep it functioning properly. Without them, the body would be unable to perform its necessary functions. Understanding the roles of each organ is essential for maintaining good health.
Development of Organs
Organ development begins early in embryonic development, with the development of the three germ layers that form during gastrulation. From these germ layers, organs are formed through a process called organogenesis. During organogenesis, cells become specialized to form specific organs and their associated tissues. The organs are then connected to the body through a process called vasculogenesis, which is the formation of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. As organs continue to develop, they are able to interact with other organs and the body to form complex systems, such as the cardiovascular, endocrine, and nervous systems. In addition to the germ layers, organs are also formed through the process of differentiation, which is the process by which cells become specialized for particular functions. Differentiated cells can then come together to form organs and organ systems. By understanding the different processes involved in organ development, scientists can better understand how organs form and function in the body.
Diseases of Organs
Our bodies are made up of many organs, each with its own unique purpose. While organs generally perform their intended function, there can be times when they become damaged or diseased. Diseases of the organs can range from mild to severe, depending on the organ and the type of disease.
The most common diseases of the organs are cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. Cancer is a condition where cells in the body grow out of control and form tumors. Heart disease is a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, leading to heart failure. Diabetes is a condition where the body does not produce enough insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Other diseases of the organs include neurological disorders, kidney disease, and liver disease. Neurological disorders involve damage or disruption of the nervous system. Kidney disease is a condition where the kidneys are unable to filter out waste from the body. Liver disease is when the liver is unable to properly process toxins.
These conditions can be treated, but prevention is the best way to avoid them. Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help prevent many of these conditions. It is also important to get regular check-ups and follow-up visits to ensure that any potential health issues are caught early.
FAQs About the What Are Organs?
1. What is an organ?
An organ is a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or set of functions in the body. Examples of organs found in the human body include the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, and stomach.
2. What is the difference between an organ and a tissue?
Tissues are composed of cells that are specialized for a particular function. Organs are made up of multiple types of tissues that work together to carry out a specific function or set of functions.
3. How many organs are in the human body?
The human body contains over 80 different organs. Some of the more prominent organs are the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, and stomach.
Conclusion
In conclusion, organs are a vital part of the human body and are responsible for many of the body’s functions. Organs are made up of different types of tissues and cells that work together to perform specific tasks. The organs of the body are essential for life and health, and any disruption of their functioning could lead to serious health issues. As such, it is important to take care of our organs and to understand how they work.