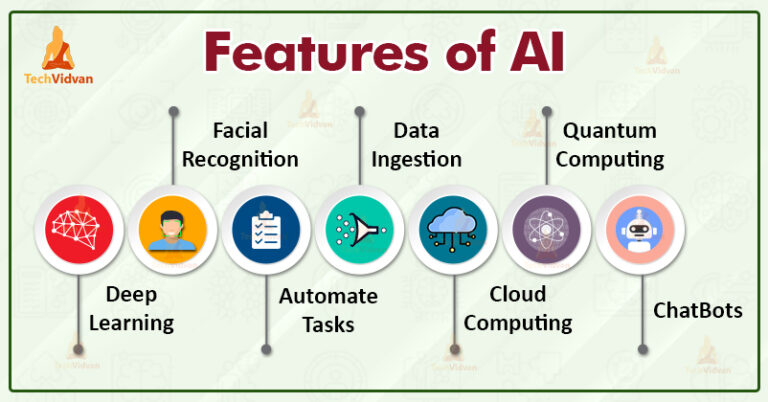
What Are 3 Examples Of Properties?
Properties are characteristics or attributes that describe something. They can be physical, chemical, or biological and can be used to describe a wide range of objects, from animals and plants to materials and machines. Three examples of properties include mass, volume, and density. Mass is the amount of matter in an object, volume is the amount of three-dimensional space an object occupies, and density is the mass per unit volume of an object.
Definition of Property
Property is a term used in legal and economic contexts to describe an asset or object that is owned or controlled by an individual or group. In the broadest sense, property can be anything that is tangible or intangible, owned by a person or organization. In a legal context, it can refer to the rights and obligations associated with ownership of a particular asset. In an economic sense, it can refer to a type of economic asset that has an intrinsic value.
There are three main types of property: real property, personal property, and intellectual property. Real property includes land, buildings, and any improvements made to the land. Personal property refers to items owned by an individual, such as furniture, clothing, and jewelry. Intellectual property includes inventions, designs, and creative works, such as books, music, and software.
Each type of property has a distinct set of legal rights and obligations associated with it. Real property is typically subject to taxes, zoning regulations, and other restrictions. Personal property is generally protected by laws that govern trespass, theft, and conversion. Intellectual property is usually subject to copyright, patent, and trademark laws.
In conclusion, property is an asset or object that is owned or controlled by an individual or group. There are three main types of property: real property, personal property, and intellectual property. Each type of property has its own distinct set of legal rights and obligations.
Types of Property
Property is a broad term that can refer to a wide range of assets and possessions. In the legal sense, property can refer to tangible objects such as land, vehicles, and physical items like furniture and jewelry. It can also refer to non-tangible assets such as stocks, bonds, and intellectual property. Understanding the different types of property can help you better manage your assets and plan for the future. Here are three examples of properties, and some tips on how to make the most of them.
Real Estate Property: Real estate property includes land, buildings, and any improvements on the land. This type of property is often held for investment purposes, and can come with many tax benefits. When buying a property, it’s important to research the area, assess the condition of the property, and be aware of any zoning requirements that may affect your ability to use the property.
Personal Property: Personal property includes tangible items that are owned by an individual, such as furniture, jewelry, clothing, and vehicles. Although these properties are usually easier to manage than real estate, they can still come with tax liabilities and require you to keep accurate records.
Intellectual Property: Intellectual property refers to the intangible assets that are created by an individual or organization, such as trademarks, copyrights, and patents. This type of property can be extremely valuable and has the potential to increase in value over time, so it’s important to protect it. If you have intellectual property, it’s important to register it and make sure that you have a clear understanding of how it is being used and what rights you have over it.
While it’s important to understand the different types of properties, it’s also important to be aware of your options when it comes to managing and protecting them. Investing in the right type of property can be a great way to increase your wealth and financial security, but it’s important to make sure that you understand the risks and responsibilities that come with it. With the right knowledge and strategies, you can make the most of your properties and maximize their value.
Examples of Real Property
, Personal Property, and Intangible Property
Real estate, personal possessions, and intangible assets are all examples of properties that can be owned. Knowing the various types of properties and how they are defined can be helpful for those considering taking on ownership of them.
Real property, also known as real estate, is a tangible asset that is normally a physical structure, such as a house, apartment, or office building. Real property can also include any land that the structure sits on, including the natural resources, such as trees, minerals, and water.
Personal property, on the other hand, is any tangible asset that is owned by an individual and can be moved from one place to another. Examples of personal property include vehicles, jewelry, furniture, and clothing.
Finally, intangible property is property that does not have a physical form, such as intellectual property, patents, copyrights, and trademarks. These types of property are intangible because they are based on ideas and concepts, not physical items.
In summary, there are three main types of properties: real property, personal property, and intangible property. Each of these types of property can provide different benefits and should be understood before taking on ownership.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chemical-properties-of-matter-608337-v33-5b6334d346e0fb0082054666.png)
Examples of Personal Property
Personal property, also known as movable property, consists of any tangible items owned by an individual or company. This includes items such as furniture, vehicles, clothing, jewelry, tools, artwork, and collectibles. Personal property can be divided into three main categories – tangible, intangible, and real property. Tangible personal property is physical assets such as furniture, vehicles, and jewelry. Intangible personal property is an asset that lacks physical form but can be assigned a monetary value such as copyrights, patents, and trademarks. Real property is land or anything attached to land. Examples of real property include houses, buildings, and other structures.
Understanding the three different types of personal property is important for understanding ownership rights and responsibilities. Whether you own a house, a car, or a piece of jewelry, it’s important to know exactly what kind of property you own in order to ensure you are taking proper care of it and protecting your investment. Knowing the types of property is also important for legal purposes, such as when making a will or filing insurance claims.
Examples of Intellectual Property
, Physical Property, and Personal Property
Property is an umbrella term for any rights or interests that one has in any object, tangible or intangible. These can range from physical possessions to intellectual and personal assets. Here are three prominent examples of property.
Intellectual property (IP) includes creations of the mind, such as inventions, literary and artistic works, and designs. IP is protected by copyright, trademarks, and patents, and can be bought and sold.
Physical property is any tangible asset owned by an individual or business. This includes land, buildings, and vehicles, as well as any goods or items of value.
Personal property refers to items of personal use, such as clothes, furniture, jewelry, and other possessions. Unlike physical property, personal property is not necessarily attached to land or buildings.
Property is an important aspect of any individual or business’s assets, and understanding the different types of property is essential for both personal and business success. Knowing the types of property, their associated rights, and how to protect them are all important considerations when handling any kind of asset.
Tax Implications of Property Ownership
Property ownership can be a great way to generate income and build wealth over time. However, it’s important to understand the tax implications of owning property. Depending on the type of property you own and how you use it, there are a number of different tax breaks and other considerations you should be aware of. In this article, we’ll take a look at three examples of how different types of property can affect your taxes.
First, if you own residential rental properties, the income you earn from those properties is subject to income tax. You can deduct expenses associated with maintaining the property, such as repairs and maintenance, property taxes, and insurance. You can also deduct mortgage interest payments and depreciation of the property.
Second, if you own commercial property, the income you earn from that property is subject to income tax. However, you may also be eligible for certain deductions related to the purchase and operation of the property, such as depreciation and amortization. Additionally, you may be able to take advantage of special tax incentives or tax credits related to the ownership of the property.
Finally, if you own agricultural property, you’re likely eligible for various tax incentives and deductions related to the operation of the property, such as farm income averaging, conservation easements, and acceleration of depreciation. Additionally, you may be able to take advantage of special tax credits or deductions related to the conservation and management of the property.
Overall, it’s important to understand the tax implications of owning property. Different types of property can have different tax implications, so make sure to consult a tax professional for the most up-to-date information.
FAQs About the What Are 3 Examples Of Properties?
Q1: What are properties in real estate?
A1: In real estate, properties refer to land and anything permanently attached to it, such as buildings, structures, and other improvements.
Q2: What are some common examples of properties?
A2: Common examples of properties include residential homes, commercial buildings, industrial warehouses, and vacant land.
Q3: What are the differences between real and personal properties?
A3: Real property is attached to land, while personal property is anything that is not attached to land. Examples of personal property include furniture, vehicles, and jewelry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, properties refer to the characteristics or attributes of an object, such as size, shape, color, texture, and density. Three examples of properties include volume, mass, and elasticity. Understanding the properties of an object helps us to better understand how the object behaves in different situations.