Is Wi-Fi Faster Than Ethernet?
Wireless technology has become commonplace in today’s digital world, and Wi-Fi is a technology that has revolutionized how we access the internet. But is Wi-Fi faster than Ethernet? This is a common question among people who are looking to upgrade their home networks. The answer depends on the type of connection and the type of device being used. Generally speaking, Ethernet is faster than Wi-Fi, but this does not necessarily mean that it is always the best choice. It is important to consider the type of connection, the speed of the connection, the environment, and the type of device being used when deciding if Wi-Fi or Ethernet is the better choice for a home network.
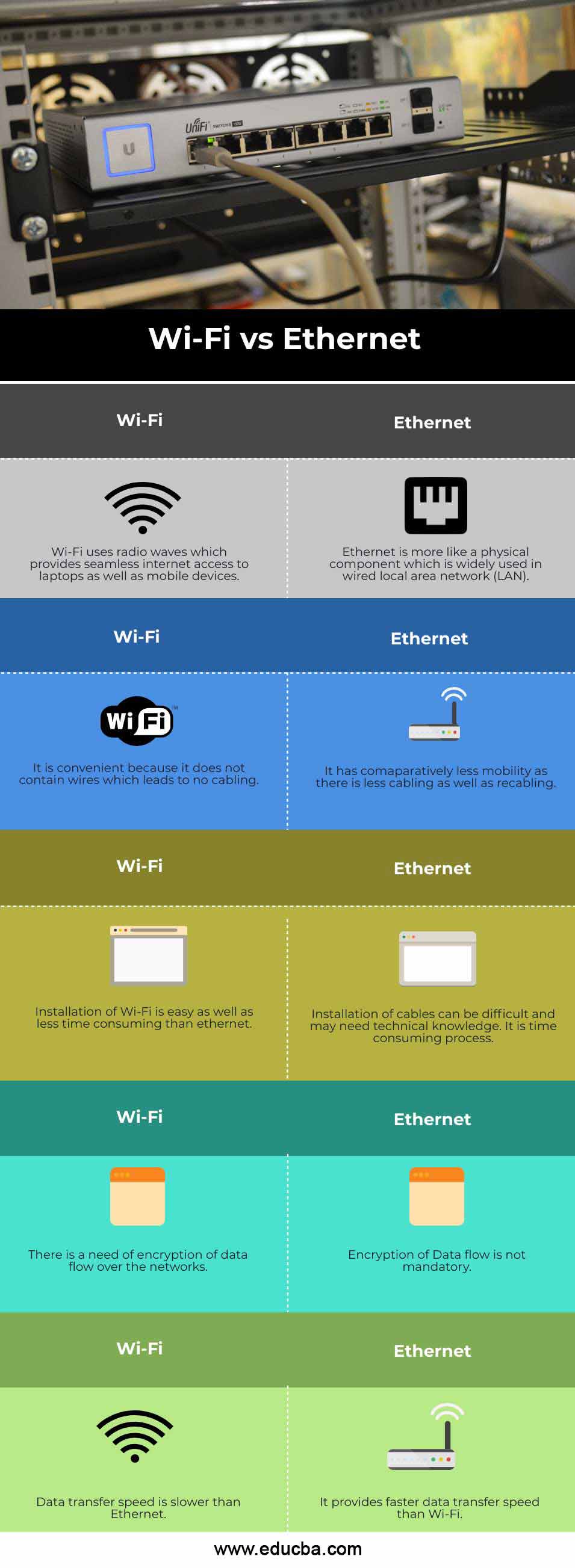
What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi is a wireless communication technology that uses radio waves to transmit data between two devices. It is the most commonly used form of wireless communication technology and is used in homes, businesses, and public spaces to provide internet access. Wi-Fi networks are secured through encryption and authentication protocols, ensuring that data is sent and received securely. Wi-Fi networks are becoming increasingly popular as they provide a convenient way to access the internet without the need for physical cables.
However, Wi-Fi is not always the fastest way to access the internet. While Wi-Fi networks can provide faster speeds than traditional Ethernet connections, the speed of a Wi-Fi connection can vary based on the distance between the device and the router, the number of users connected to the network, and other environmental factors. As such, it is important to understand the pros and cons of using Wi-Fi to access the internet before making a decision on the best connection type for your needs.
What is Ethernet?
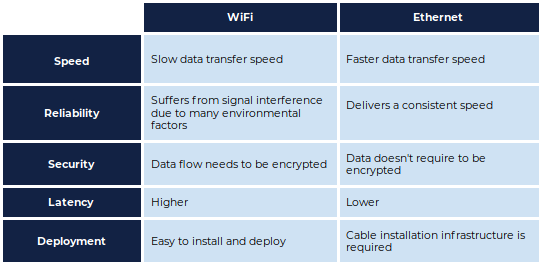
Ethernet is a local area network (LAN) connection that is used to transfer data from one device to another. It is a wired connection that uses cables to connect two or more devices. It is typically used to connect computers, routers, and printers to the internet, but can be used to connect any type of device. Ethernet is typically considered to be faster than Wi-Fi because it offers more consistent speeds, fewer connection issues, and a more secure connection. The main benefit of Ethernet is that it is a reliable and secure connection that is not subject to interference or congestion from other Wi-Fi networks in the area. Ethernet also offers speeds up to 10 times faster than Wi-Fi, making it the ideal choice for streaming and gaming.
What Factors Determine the Speed of Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi is a wireless technology that enables devices to connect to the internet. But is it faster than Ethernet, the traditional wired connection? The answer isn’t so simple. While Wi-Fi can be faster than Ethernet in some cases, there are several factors that determine the speed of a Wi-Fi connection, including the type of device, the wireless frequency, the distance from the router, and the interference from other sources.
To start, the type of device you are using is an important factor in determining the speed of your Wi-Fi connection. For example, some devices may not be able to take advantage of the latest Wi-Fi standards, which can result in slower speeds. Also, the wireless frequency you are using is important. Most Wi-Fi routers use the 2.4 GHz frequency, which can be slower than the 5 GHz frequency used by newer routers.
Distance from the router and interference from other sources can also play a role in determining Wi-Fi speeds. The farther away you are from the router, the weaker the signal and the slower the connection. Additionally, the presence of other wireless devices, such as microwaves, cordless phones, and baby monitors can cause interference and reduce the speed of the Wi-Fi connection.
Ultimately, the speed of a Wi-Fi connection is determined by a variety of factors. Knowing what factors can affect your Wi-Fi connection can help you optimize your setup for faster speeds and better performance.
What Factors Determine the Speed of Ethernet?
When it comes to the speed of Ethernet, there are several factors that come into play. These include the type of Ethernet cable being used, the quality of the cable, the length of the cable, and the type of network being used. The type of Ethernet cable being used will determine the speed of data transfer; for example, a Cat5e cable can transfer data up to 1 gigabit per second (Gbps), while a Cat6 cable can transfer data up to 10 Gbps. The quality of the cable is also important; a good-quality cable will ensure the data is transferred quickly and efficiently. The length of the cable is also an important factor, as a longer cable will slow the speed of data transfer. Finally, the type of network being used can also affect the speed of data transfer; for example, a wired network is typically faster than a wireless network.
By understanding these factors, you can determine which type of connection is best for your needs. If you are looking for a fast and reliable connection, the wired connection of Ethernet is your best bet. However, if you are looking for a more convenient connection that is still fast, then a wireless connection such as Wi-Fi may be the way to go. Ultimately, the decision of which connection is the best for your needs depends on several factors and should be evaluated on an individual basis.
How Do Wi-Fi and Ethernet Compare?
When it comes to connecting your devices and networks, you have two main options: Wi-Fi and Ethernet. But which one is better? To answer that question, it’s important to understand how the two technologies compare.
Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, is a technology that allows two or more devices to communicate wirelessly. Wi-Fi networks consist of routers and access points connected by radio waves. This makes it easy to connect devices without the need for physical cables.
Ethernet, on the other hand, is a wired technology that requires physical cables to connect devices. Ethernet is typically faster and more reliable than Wi-Fi, but it requires additional equipment such as routers, hubs, and switches.
When it comes to speed, Ethernet is generally faster than Wi-Fi. This is because Ethernet is a wired connection, while Wi-Fi is a wireless connection. Wi-Fi is also subject to interference from other devices, which can slow down speeds. However, Wi-Fi networks are more convenient and easier to set up, and they don’t require additional equipment.
Ultimately, the decision between Wi-Fi and Ethernet comes down to your needs. If you need fast, reliable connections, then Ethernet is the way to go. But if convenience and ease of setup are more important, then Wi-Fi is the better choice.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Wi-Fi and Ethernet?
Wi-Fi and Ethernet are two of the most popular technologies for creating and maintaining a computer network. Both have their own advantages and disadvantages, and it can be difficult to decide which is the best option for a particular network. When it comes to speed, it is important to consider both the theoretical maximum speeds of each technology, as well as the actual speeds that can be achieved in a real-world environment.
Wi-Fi is typically faster than Ethernet, with speeds ranging from 54 Mbps up to 10 Gbps. This means that it is capable of handling most applications, including streaming HD video and online gaming. However, real-world speeds tend to be much lower than this, and can vary significantly depending on the number of devices connected to the network, the strength of the signal, and other factors.
Ethernet is a reliable technology that offers speeds of up to 10 Gbps, but real-world speeds tend to be much lower than this. It is typically used for more static networks where the same devices are connected all the time, such as in an office or factory. Ethernet is also more secure than Wi-Fi, as it is harder for unauthorized users to access the network.
When deciding between Wi-Fi and Ethernet, it is important to consider the advantages and disadvantages of each technology, as well as the speeds that can be achieved in a real-world environment. The right choice will depend on the specific needs of the network.
FAQs About the Is Wi-Fi Faster Than Ethernet?
1. How much faster is Wi-Fi than Ethernet?
Answer: Wi-Fi can be up to 10 times faster than Ethernet depending on the type of router and connection.
2. Does Wi-Fi always provide faster speeds than Ethernet?
Answer: No, Wi-Fi speeds can vary depending on the router, the distance between the router and the device, and the number of devices connected to the network.
3. What can I do to increase my Wi-Fi speeds?
Answer: You can try to increase the signal strength of your router by moving it to a more central location in your house, or by using a Wi-Fi extender. Additionally, you can reduce the number of devices connected to the network for a faster connection.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the speed of Wi-Fi and Ethernet are both dependent on the network they are connected to. However, in general, Ethernet is considered to be faster and more reliable than Wi-Fi. Ethernet also provides a more secure connection, making it the preferred choice for businesses and large organizations. For the average user, Wi-Fi is usually the most convenient option because it allows you to access the internet from anywhere in your home or office.