Is There A 1G Network?
The 1G network is a type of cellular network technology that was the first generation of mobile networks. It was introduced in the 1980s and developed rapidly throughout the decade. 1G networks were analog-based and used low frequencies to transmit voice calls. They operated on the traditional cellular network system, where a user’s calls were routed through a network of towers. This technology allowed for widespread coverage and was the first step in allowing mobile phones to become a staple in modern life. 1G networks are no longer used, as they have been superseded by faster and more efficient 2G, 3G, and 4G networks; however, they remain an important part of the history of mobile communication.
What is the 1G Network?
The 1G Network, also known as the first generation network, is a cellular network technology that was introduced in the 1980s. This technology allowed people to make and receive calls with their mobile phones. It was the first widely used cellular network that enabled voice calls and text messaging. Despite the development of newer, more advanced technologies, the 1G Network is still in use in some parts of the world.
The 1G Network uses analog transmission technology, which is considered outdated by today’s standards. This technology has limited capacity and bandwidth compared to newer technologies, such as 2G, 3G, and 4G. It was designed to provide basic communication services such as voice calls and short text messages, but not the type of data-intensive services available today.
Despite its limitations, the 1G Network is still used in some remote areas where newer technologies are not available. It has also been used in developing countries to provide basic communication services to people who would not otherwise have access to them.
In conclusion, the 1G Network is an outdated technology that is still in use in some parts of the world. It is limited in its capacity and bandwidth compared to newer technologies, and is primarily used to provide basic communication services to people in remote areas or developing countries.
What are the Benefits of the 1G Network?
The 1G Network, or First Generation Network, is the first-ever mobile phone network. It was first used in the 1980s and was limited to analog technology. This network introduced the world to the modern mobile phone and was a major breakthrough in communication technology. Since then, the mobile phone industry has grown exponentially and the technology has advanced at a rapid pace.
The 1G Network offers several benefits that have made it a popular choice for businesses, governments, and individuals. For businesses, the 1G Network provides a secure connection that is not easily disrupted. It also provides an efficient and reliable way of making calls, sending text messages, and accessing the internet. Governments also rely on the 1G Network for reliable communication and data transmission.
Individuals benefit from the 1G Network because it provides a secure and reliable connection for their mobile devices. It also provides a stable connection with good call quality and low latency. Additionally, the 1G Network is more affordable than other mobile networks, making it an attractive option for those on a budget.
Overall, the 1G Network has revolutionized the mobile phone industry and has provided users with reliable and secure connections. The 1G Network is a great option for those who want reliable connections and an affordable way to stay connected.
What Companies Offer 1G Network Services?
The 1G network is an antiquated technology, but it still exists in certain areas. It is the first generation of cellular network technology and is still used in some parts of the world. If you’re curious to know if your area is covered by a 1G network, then you should read on to find out more.
Generally speaking, 1G networks are limited in speed and bandwidth. Despite this, some companies still offer 1G services, and it is still used in some countries. Telstra in Australia, for example, offers 1G services as a standard option for those who don’t need high bandwidth. Meanwhile, in Russia, the 1G network is still used in some rural areas.
In the US, the most popular 1G network is AT&T’s 2G network, which still provides service to some rural areas. However, it is important to note that 2G and 1G networks are not the same. 2G networks provide faster speeds and offer more bandwidth than 1G networks.
For those who need high-speed internet, a 1G network is not the best option. However, for those who are looking for affordable solutions, 1G networks are still a viable option. It is important to keep in mind that 1G networks are not as reliable as newer networks, so you should make sure that you have a backup plan in place in case the 1G network fails.
Overall, 1G networks are still available in some areas, and some companies still offer 1G services. It is important to note that 1G networks are not as reliable or fast as newer networks, but they are still an affordable option for those who need internet access on a budget.

What are the Limitations of the 1G Network?
1G network technology is the first generation of cellular technology and is based on analog signals. It was first introduced in the 1980s and is no longer used by most cellular networks. As the first cellular network technology, it had several limitations, including a lack of security, limited capacity for data, and unreliable service in some areas.
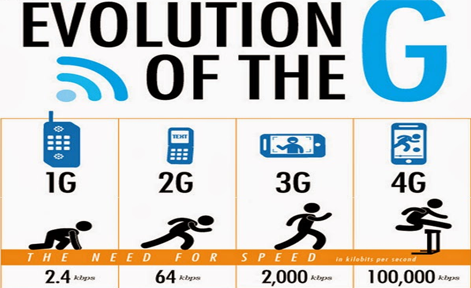
Security was a huge issue for 1G networks because the digital encryption and authentication protocols that are the standard today did not exist. This meant that anyone could potentially intercept voice and data communications. Additionally, the capacity for data was limited, as 1G networks could only transfer data at a rate of 2.4 Kbps. This was suitable for voice calls but not for data-heavy applications like streaming video.
Finally, 1G networks were prone to interference from other radio signals, such as cordless phones and ham radio operators. This could cause dropped calls and poor service in some areas. As such, 1G networks were eventually replaced by newer, more reliable generations of cellular technology.
How Does the 1G Network Compare to Other Network Technologies?
In the world of telecommunications, 1G networks represent the first generation of mobile networks. This technology is a precursor to other generations of cellular networks, such as 2G, 3G, and 4G. While 1G networks offer a slower speed than the other generations, they remain an important part of the telecommunications landscape.
1G networks are well-suited for voice calls and can offer data speeds up to 2.4Kbps. Compared to 2G, 3G, and 4G networks, 1G is a much slower technology and is not suitable for data-intensive applications. 1G networks are also more prone to interference and have a limited coverage area when compared to more modern cellular networks.
Despite the limitations of 1G networks, they are still used in some areas of the world. 1G is the only technology available in some remote locations, where the cost of upgrading to a more modern cellular network is prohibitively expensive. Additionally, some legacy applications, such as short messaging service (SMS), are still supported by 1G networks.
The 1G network is the predecessor of current cellular networks, and while it may not be suitable for data-intensive applications, it still serves a purpose in some parts of the world. It is important to understand the advantages and disadvantages of 1G networks so that businesses can make informed decisions about their communication networks.
What are the Future Prospects for the 1G Network?
The 1G network was the first generation cellular network, launching in the early 1980s. It laid the foundation for digital cellular networks that would follow, but has since been largely replaced by more advanced and efficient networks. But despite its age, the 1G network still has its uses. While the speed of the 1G network is far too slow for most modern applications, its reliable connection and low cost make it ideal for certain applications.
Looking ahead, the 1G network may have a place in the future. The low cost of operation and reliability make it an attractive option for low-intensity applications, such as those used for medical monitoring or asset tracking. Additionally, the 1G network’s ability to provide reliable service in areas with poor cellular coverage could be utilized in the Internet of Things (IoT). As technology advances, the 1G network may be used to fill the gaps in coverage and provide reliable, low-cost connections.
Overall, the 1G network is an outdated technology that has been largely replaced by newer technologies. However, its low cost and reliability may make it an attractive option for certain applications in the future. With advances in technology, the 1G network may continue to have a place in the world of digital communication.
FAQs About the Is There A 1G Network?
1. What is a 1G network?
A 1G network is the first generation of cellular network technology. It was first introduced in the 1980s and was the first widely available cellular network to support voice calls.
2. Does my phone need to be compatible with a 1G network in order to use it?
No, your phone does not need to be compatible with a 1G network in order to use it. Any modern phone will be able to use a 1G network if it is available in your area.
3. What are the advantages of using a 1G network?
The main advantage of using a 1G network is that it is incredibly reliable and is not prone to the same issues that newer networks can experience. Additionally, 1G networks are significantly cheaper to set up than newer networks.
Conclusion
The answer to the question “Is there a 1G network?” is yes. 1G networks are the first generation of cellular networks and are still used in many parts of the world. They are slower and less reliable than more advanced networks but are still a viable option for those on a budget or in rural areas. While the majority of the world has moved on to faster networks, 1G networks are still an important part of the telecommunications industry.