Is 1000 Mbps Faster Than 5G?
1000 Mbps, or 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps), is a measure of internet speed that is significantly faster than the speed of 5G, which is estimated to reach up to 20 Gbps. This means that 1000 Mbps is faster than 5G, but not by a large margin. However, 5G has the potential to be much faster than 1000 Mbps, as it is still in the development stages. 5G is expected to be the next big leap in mobile internet speeds, with the potential to be up to 10 times faster than current 4G speeds. With this kind of speed, 5G will be able to provide better streaming and faster downloads for users.
What is 1000 Mbps?
1000 Mbps, commonly referred to as gigabit internet, is the fastest type of internet available. It is 100 times faster than the average internet speed of 10 Mbps. It is also the fastest available home internet connection. 1000 Mbps is the speed at which data is transferred from your computer to the internet. It is measured in megabits per second (Mbps).
In comparison, 5G is an emerging technology that promises faster speeds and better performance than existing 4G networks. 5G is expected to offer speeds of up to 10 Gbps, which is roughly 100 times faster than 1000 Mbps. Furthermore, 5G will offer improved latency and network capacity, which means more devices can be connected simultaneously.
Therefore, 1000 Mbps is not faster than 5G, but it is the fastest available home internet connection. 5G is expected to be faster than 1000 Mbps, but it is not yet widely available. It is expected that 5G will become more widely available in the coming years, and that it will eventually surpass 1000 Mbps in speed.
What is 5G?
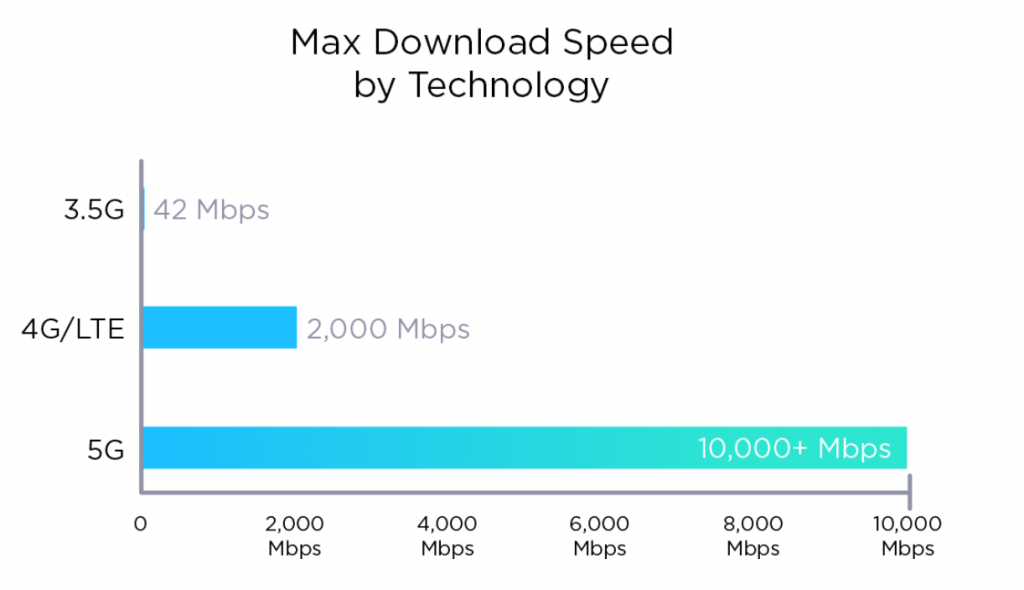
5G is the fifth generation of wireless technology, offering faster speeds and lower latency than its predecessors. This next-generation cellular technology promises to revolutionize the way we use our mobile devices. With 5G, users can access data up to 20 times faster than with 4G LTE, and latency (the time it takes for a device to send and receive data) is reduced significantly. 5G networks are also capable of supporting more devices simultaneously, allowing for better performance, faster download speeds, and lower latency.
To put it into perspective, a 5G connection can reach speeds up to 1,000 Mbps — that’s 100 times faster than the average home broadband connection. This means you can stream HD movies without buffering, download large files quickly, and enjoy lag-free gaming experiences. To give you an idea of the huge differences between 4G and 5G, 5G can provide download speeds over 1,000 times faster than 4G. So, is 1000 Mbps faster than 5G? The answer is yes — 1000 Mbps is significantly faster than 5G.
How Fast is 1000 Mbps?
With the advancement of technology, the speed of internet connection has become increasingly important. It is becoming increasingly necessary to understand the differences between the various types of internet speeds, particularly between 1000 Mbps and 5G. 1000 Mbps, which stands for 1000 megabits per second, is the fastest broadband connection that is widely available to consumers. It is significantly faster than the average broadband connection, which is currently around 30 Mbps. 1000 Mbps is capable of downloading a two-hour HD movie in just 7 minutes, which is a remarkable speed.
In comparison, 5G is the fifth-generation cellular network technology that is expected to revolutionize the telecommunications industry. It promises faster download speeds, lower latency, and increased reliability when compared to traditional cell phone technologies. It is currently being rolled out in various parts of the world, and while it has not yet reached the speeds of 1000 Mbps, it is expected to surpass it in the near future.
In conclusion, 1000 Mbps is currently faster than 5G, however, 5G is expected to catch up in the near future. 1000 Mbps is an incredibly fast speed, capable of downloading a two-hour HD movie in just 7 minutes. It is the current gold standard for internet speeds and is now widely available to consumers. 5G, on the other hand, is in the process of being rolled out and promises to revolutionize the telecommunications industry, eventually surpassing 1000 Mbps in terms of speed.

How Fast is 5G?
5G is the fifth generation of cellular technology and is set to revolutionize the way we use our devices and access the internet. 5G technology has been in development for over a decade and is now being rolled out across the world. It’s the fastest cellular technology available today and offers speeds of up to 10 Gbps, which is significantly faster than the average home internet speeds of around 100 Mbps.
5G is also faster than the previous generation of cellular technology, 4G LTE, which offers speeds of up to 1 Gbps. 5G networks are also much more reliable than 4G and offer much better coverage, so you can get a fast and reliable connection no matter where you are.
So, is 1000 Mbps faster than 5G? The answer is yes. 5G networks can offer speeds up to 10 Gbps, which is significantly faster than 1000 Mbps. However, 5G is still in its early stages and not available in all areas yet. However, in areas where 5G is available, users can experience speeds up to 10 Gbps. This makes 5G an ideal option for those who need a fast and reliable connection.
Comparing 1000 Mbps and 5G
connection speeds is an apples-to-oranges comparison. 1000 Mbps is the maximum speed of wired connections over Ethernet or coaxial cables, while 5G is a wireless-based technology that has the potential to provide ultra-fast speeds and reduced latency. To determine which is the faster connection, it depends on the infrastructure and the area you’re located in.
When it comes to connection speed, 1000 Mbps and 5G are two very different technologies, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. 1000 Mbps connections are typically used in wired networks, delivering a maximum speed of 1000 Mbps, and typically offer more consistent speeds and less interference than wireless connections. On the other hand, 5G is a wireless technology that has the potential to provide speeds of up to 20 Gbps in ideal conditions, and has the potential for significantly reduced latency compared to wired connections.
So, when it comes to speed, 5G has the potential to be faster than 1000 Mbps in certain conditions. However, it’s important to remember that 5G is still in its early stages and the technology is still developing. The actual connection speed you get on 5G networks depends on factors such as the infrastructure, the area you’re located in, and the number of users connected to the network.
In conclusion, 1000 Mbps and 5G are two very different technologies, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. While 5G has the potential to be faster than 1000 Mbps in certain conditions, the actual speed you get depends on a variety of factors. So, it’s important to assess your particular situation when deciding which technology to use.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 1000 Mbps is generally faster than 5G, but it also depends on the service provider and the location to which the service is being provided. It is important to understand that 1000 Mbps is a measure of speed, while 5G is a measure of data transfer rate. 1000 Mbps can offer higher speeds than 5G, but 5G can provide a more consistent connection and better overall performance. Ultimately, the best choice for your needs will depend on factors such as the service provider, the area in which you live, and the type of data you are transferring.
FAQs About the Is 1000 Mbps Faster Than 5G?
1. Is 1000 Mbps Faster Than 5G?
Answer: No, 1000 Mbps is a measure of broadband speed, while 5G is a cellular network technology. While 5G networks are faster than 4G, they are not faster than 1000 Mbps broadband.
2. How Much Faster Is 5G Than 1000 Mbps?
Answer: Generally, 5G networks are up to 20 times faster than 1000 Mbps broadband. However, the actual speed of 5G networks can vary depending on the coverage and network conditions.
3. What Is the Difference Between 5G and 1000 Mbps?
Answer: 5G is a cellular network technology that enables faster speeds than 4G networks, while 1000 Mbps is a measure of broadband connection speed. 5G networks are not inherently faster than 1000 Mbps, but they can deliver significantly faster speeds in certain conditions.
Conclusion
1000 Mbps is not faster than 5G. 5G technology is much faster than 1000 Mbps and has the potential to reach speeds up to 10 Gbps. 5G also offers improved latency, reliability, and capacity, making it a more attractive option for businesses and consumers alike. 1000 Mbps is still a very fast and reliable connection, but it cannot compete with the speeds and features offered by 5G.