How Many Mbps Is 4G?
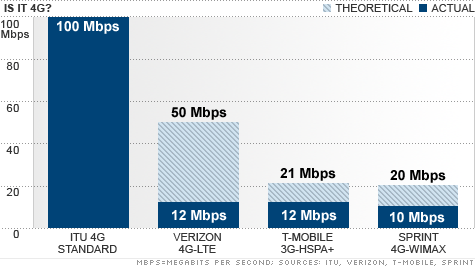
4G is the fourth generation of cellular technology and is the successor to 3G. It is a significant step up from 3G in terms of speeds, allowing download speeds up to 100 Mbps and upload speeds up to 50 Mbps. This is a major leap from the theoretical maximums of 3G, which offered download speeds of up to 21 Mbps and upload speeds of up to 5.76 Mbps. 4G also brings with it other advantages such as improved latency and better quality of service.
What Is 4G?
4G is the fourth generation of cellular mobile telecommunications technology, and is the latest standard in mobile internet connectivity. 4G is an upgrade to the 3G networks, offering faster speeds, improved reliability, and better overall coverage. It is capable of delivering download speeds of up to 100 mbps and upload speeds of up to 50 mbps, making it ideal for streaming HD video, downloading large files, and using other bandwidth-intensive applications. The increased speed and reliability of 4G networks have made them the preferred choice for mobile users across the world. With 4G, users can experience faster web browsing, faster streaming of videos and music, better voice quality, and more reliable connections. It is also capable of handling multiple simultaneous connections, making it ideal for business and enterprise use. 4G is the foundation for the next generation of mobile networks, and its continued evolution will make it an even more powerful and reliable technology.
What Is Mbps?
Mbps stands for “megabits per second” and is a unit of measure used to determine the speed of an internet connection. It is commonly used to measure the speed of downloads and uploads, and it is also used to measure the speed of mobile data networks. Mbps is a measure of the rate at which data is transferred over a network, and it is most commonly used to measure the speed of broadband and wireless networks. When it comes to 4G networks, the speeds are typically between 5-20 Mbps, depending on the coverage area and network provider. The exact speed of a 4G connection will vary depending on the network provider, the device used, and the location of the user. In general, 4G connections are typically faster than 3G connections, providing users with faster download and upload speeds.
How Fast Is 4G?
When it comes to internet speed, 4G is a step up from 3G. 4G networks provide faster download and upload speeds than 3G, allowing users to access more data faster. But just how fast is 4G? The answer depends on the network provider, the device you’re using, and the area you’re in.
Generally, 4G networks can reach speeds of up to 100 Mbps. This means that if you’re using a 4G network, you can download or upload a 1GB file in about 8 minutes. However, the actual speed of 4G networks can vary, depending on the network provider, your device, and the area you’re in.
The speed of 4G networks also depends on the type of 4G technology the network is running. For example, 4G LTE networks can reach peak speeds of up to 300 Mbps, while 5G networks can reach speeds of up to 1 Gbps.
In addition to speed, 4G networks offer improved coverage and reliability over 3G networks. This means that users can access the internet in more places than ever before.
All in all, 4G networks are the fastest and most reliable option for accessing the internet on the go. With speeds of up to 100 Mbps, 4G networks can provide blazing-fast download and upload speeds, allowing users to access more data faster. If you’re looking for the fastest option for accessing the internet, 4G is the way to go.

What Factors Affect 4G Speeds?
When it comes to cellular networks, 4G is the latest and greatest technology available. But how many Mbps can you expect from a 4G network? The answer isn’t as straightforward as it may seem. The actual speed of your 4G connection can vary depending on several factors, such as the type of network, your location, network congestion, and even the device you’re using.
The type of network you’re using can have a major impact on your 4G speeds. Generally, LTE networks are the fastest, followed by HSPA+ and UMTS networks. Some networks are equipped with multiple frequency bands, which can also affect your speeds. Additionally, if you’re in an area without 4G coverage, you may have to revert to 3G speeds or even slower.
Your location can also play a big role in your 4G speeds. If you’re in a densely populated area, you may experience slower speeds due to network congestion. On the other hand, if you’re in a rural area, you may experience faster speeds due to fewer people using the network.
The device you’re using can also affect your 4G speeds. Older devices may not be able to take advantage of all the features of a 4G network, resulting in slower speeds. If you’re using a newer device, however, you should be able to get the full speed of the 4G network.
Ultimately, the answer to the question, “How many Mbps is 4G?” depends on a variety of factors. The type of network, your location, network congestion, and the device you’re using can all play a role in your 4G speeds. So, if you’re looking for the fastest 4G speeds, it’s important to consider all of these factors.
What Is the Difference Between 4G and 5G?
The term 4G and 5G refer to the generations of cellular networks. 4G is the fourth generation of mobile networks and 5G is the fifth. The main difference between 4G and 5G is the speed. 4G is capable of providing download speeds up to 100 Mbps and upload speeds up to 50 Mbps, while 5G offers peak download speeds of up to 10 Gbps and peak upload speeds of up to 6 Gbps.
With 5G, users will experience faster data transfer speeds, improved latency, and increased network capacity. This means they can stream videos, send and receive large files, and use the internet more efficiently. 5G also has the potential to enable new use cases such as massive machine-type communication, connected vehicles, and augmented reality.
In contrast, 4G is still considered a reliable network for most users. It offers good coverage and speeds that are fast enough for streaming videos, downloading files, and playing online games. However, as more people use 4G networks, the connection may slow down due to the high demand.
Both 4G and 5G are important technologies that offer users reliable and fast connection speeds. 4G is suitable for most users, while 5G is the future of mobile networks and will provide an even better experience.
What Is the Future of 4G?
From streaming movies to video calls, 4G has revolutionized the way we use the internet. As we look to the future, improvements in 4G technology and the introduction of 5G are anticipated to bring even more changes. With faster speeds and greater data capacity, 4G networks have changed the face of the digital world and with 5G, the possibilities are even greater.
So, what does the future of 4G networks hold? As the demand for high-quality data connections continues to increase, network providers are investing in modernizing their infrastructure and increasing the number of towers in order to optimize 4G speeds. This will help ensure that the connection is reliable and efficient for users, regardless of where they are.
In addition to improving the existing 4G networks, tech companies are also looking to the future of 5G technology. With 5G networks, users can expect to experience faster download speeds, lower latency, and better connection quality. As 5G becomes more widely available, the possibilities for using 4G networks will continue to expand and increase.
Overall, the future of 4G networks looks bright. As more people become aware of the advantages of using 4G networks, demand will continue to increase and providers will continue to invest in modernizing their infrastructure. This will help ensure that users can enjoy the benefits of faster speeds and better connections for years to come.
FAQs About the How Many Mbps Is 4G?
1. How fast is 4G compared to 3G?
A: 4G is significantly faster than 3G, with typical speeds of around 10 Mbps for downloads and 5 Mbps for uploads.
2. Is 4G speed consistent?
A: The speed of 4G can vary depending on the network traffic in the area, as well as the number of devices connected to the network.
3. What is the peak 4G speed?
A: The peak 4G speed is typically around 70 Mbps for downloads and 40 Mbps for uploads.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 4G is capable of providing download speeds of up to 100 Mbps and upload speeds of up to 50 Mbps. While these speeds are still significantly lower than 5G, they are still much faster than 3G and allow for a much faster internet connection than before. 4G is the current standard for cellular data connection speeds and is available in most parts of the world.